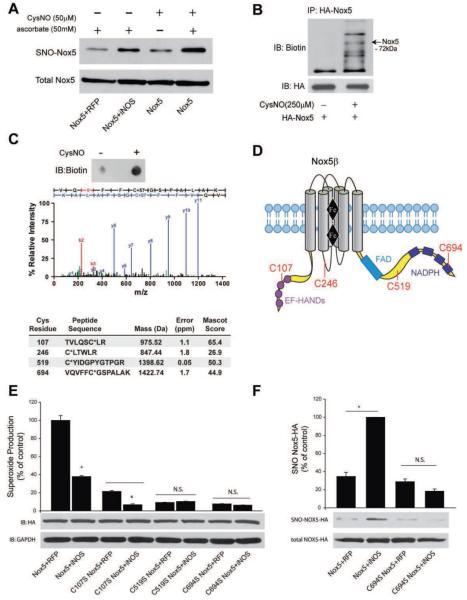
Figure 7. iNOS increases the S-nitrosylation of Nox5.
COS-7 cells were transfected with Nox5 and either control (RFP) or iNOS. 48h post-transfection, cells were either not treated or treated with CysNO and the S-nitrosylation of Nox5 determined via the biotin switch assay in the presence and absence of asorbate. Biotinylated proteins were concentrated by streptavidin-agarose and immunoblotted for HA (SNO-Nox5, upper panel) versus immunoblotting for HA in total cell lysates (total Nox5, lower panel). (B) COS-7 cells expressing Nox5 were exposed to CysNO, lysed, the biotin switch assay performed and Nox5 immunoprecipitated via the HA-tag. Immune complexes were immunoblotted with anti-biotin antibody (upper panel) and then reprobed for total Nox5 (HA, lower panel) under non-reducing conditions. (C) MS/MS spectrum of Cys694-carbidomethylated tryptic peptide isolated from HA-Nox5 expressing COS-7 after CysNO treatment (see Methods). The b- and y-series ions are in red and blue, respectively.) Summary of Cys-containing Nox5 peptides identified from CysNO-treated COS-7 following biotin switch assay and LC-MS/MS analysis, including mass and error of parent ion, and Mascot ion score. Asterix indicates the site of carbidomethylation. (D) Geographical illustration of the sites of Nox5 S-nitrosylation. (E) Relative production of superoxide from Nox5 WT, C107S, C519S and C694S in the presence and absence of iNOS. Results are presented as % of control (means ± S.E., n =6 * p<0.05 versus RFP). (F) The S-nitrosylation of Nox5 WT and C694S was detected via the biotin switch assay. Biotinylated proteins were concentrated by streptavidin-agarose and immunoblotted for HA (SNO-Nox5, upper panel) versus HA in total cell lysates (total Nox5, lower panel). The relative densitometry of SNO:total HA is shown as a % of the maximum (means ± S.E., n =3 * p<0.05).