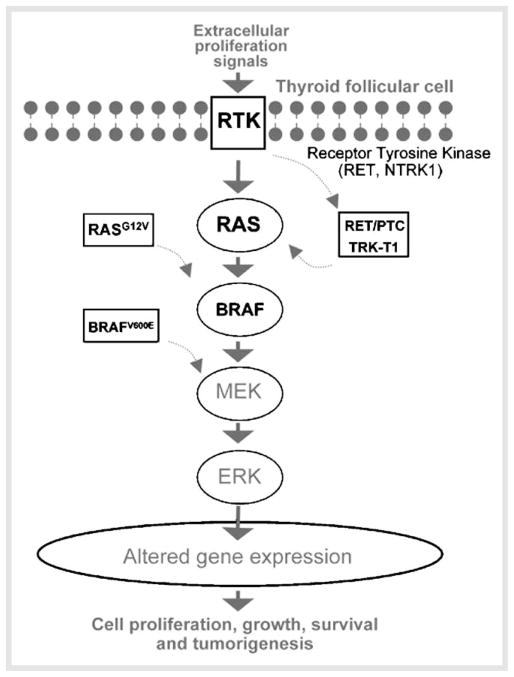
Fig. 2.
Aberrant activation of the MAPK signaling pathway in papillary thyroid tumor cells. In normal follicular cells, binding of proliferation signal molecules to membrane receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) such as RET and NTRK1 leads to receptor phosphorylation and activation of the downstream effector RAS. The phosphorylation cascade in the downstream effectors leads to the translocation of ERK to the nucleus to affect genes involved in cell differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, and survival. In PTC, fusion genes such as RET/PTCs and TRK-T1 and mutated genes such as BRAFV600E and RAS constitutively activate MAPK signaling, thereby leading to the development of carcinogenesis.