Figure 3.
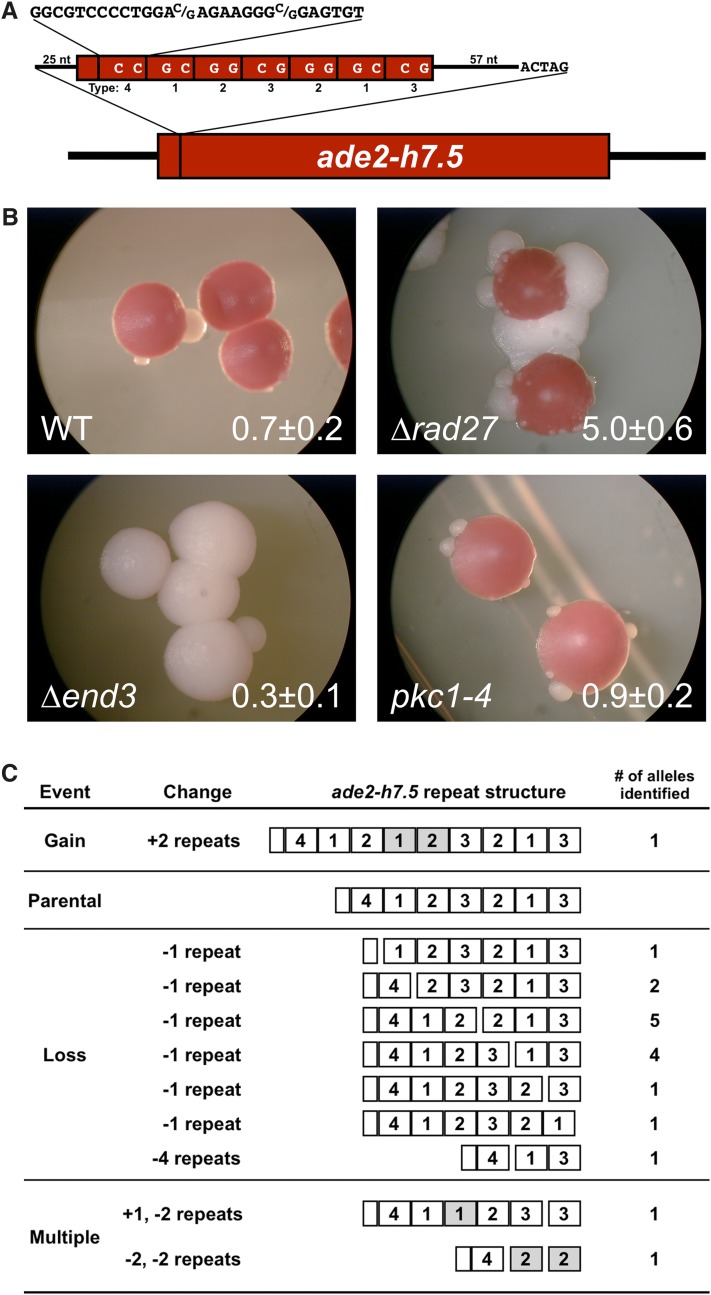
The color-based ade2-h7.5 reporter was used to identify factors that regulate the stability of the human HRAS1 minisatellite. (A) The ade2-h7.5 allele. Seven and one-half repeats of 28 bp derived from the human HRAS1 minisatellite were inserted into ADE2 at the XbaI site. With unique flanking DNA and a 6 bp duplication of the XbaI site, the insert is 301 bp long, resulting in a frameshift that disrupts ADE2. As shown, repeats vary at the 14th and 22nd nucleotide. Type 1 repeats contain a G at position 14 and a C at position 22, Type 2 repeats contain G at both, Type 3 are C G, and Type 4 contain C at both. (B) Red/white color segregation in ade2-h.75 strains. Strains were grown at 30° for 3 days, and then at room temperature for 4 days. The wild-type ade2-min3 parent is DTK1188. Construction of the following strains is described above: rad27Δ (DTK1225), end3Δ (DTK1373), and pkc1-4 (DTK1375). Note the presence in the rad27Δ strain of both blebs and sectors in the upper-right of the top colony. (C) Altered alleles of ade2-h7.5 from 18 independent bleb isolates of DTK1225 (ade2-h7.5 rad27Δ) were sequenced. Altered allele structures are shown using the repeat number designations from the parental allele in Figure 3A. Repeats shown in gray have been added or modified. The location of deletions is illustrated as a gap in the repeat tract. For consistency, added repeats are shown to the right of the repeats they duplicate, although it is not possible to distinguish added and original repeats in the sequence.