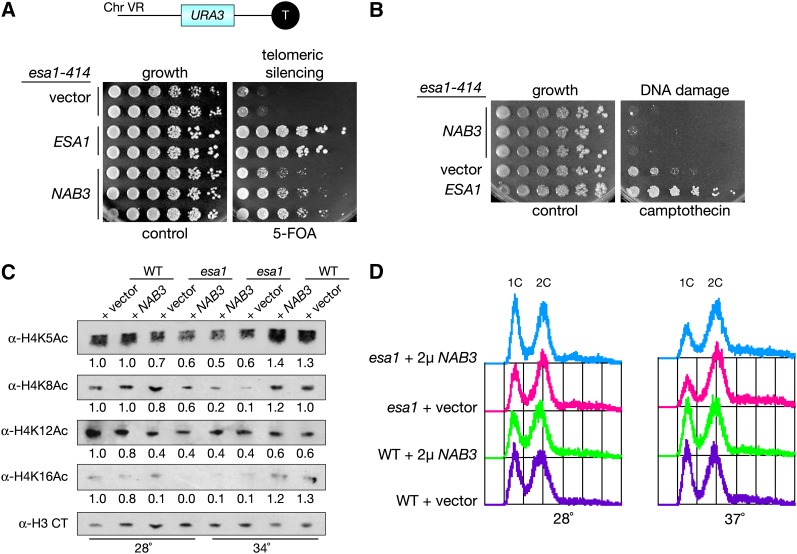
Figure 3 .
Overexpression of NAB3 affects multiple esa1 mutant phenotypes. (A) Top: Diagram of TELVR::URA3 telomeric silencing marker on the right arm of chromosome V. Bottom: Increased gene dosage of NAB3 suppresses the esa1 5-FOA sensitivity in this assay. An esa1 strain with the TELVR::URA3 reporter (LPY4919) was transformed with vector (pLP271), ESA1 (pLP798), or NAB3 (pLP1310), and plated on SC-Trp (growth) with and without 5-FOA (telomeric silencing) at 33°. (B) Increased gene dosage of NAB3 exacerbates esa1’s sensitivity to the DNA damaging agent camptothecin. An esa1 strain (LPY4774) was transformed with vector (pLP326), ESA1 (pLP796), or NAB3 (pLP2018), and plated on SC-Ura with DMSO (growth) and 20 µg/ml camptothecin (DNA damage). (C) Overexpression of NAB3 does not increase global acetylation levels of H4K5, H4K8, H4K12, or H4K16 in esa1 mutants. Whole-cell extracts were made from wild-type (LPY5) and esa1 (LPY4774) strains with vector (pLP362) or 2μ NAB3 (pLP2018) grown in SC-Ura media at both permissive (28°) and elevated (34°) temperatures. These were immunoblotted for amounts of isoform-specific H4 acetylation and total H3. An H3 reprobe was performed for each individual H4 acetylation blot. Quantification data shown are normalized for H3 loading. (D) Overexpression of NAB3 does not influence esa1’s G2/M cell-cycle block. The same strains as in (C) were grown at 28° and shifted to 37° for 4 hr before fixing and staining with propidium iodide. Cell-cycle profiles were analyzed by flow cytometry.