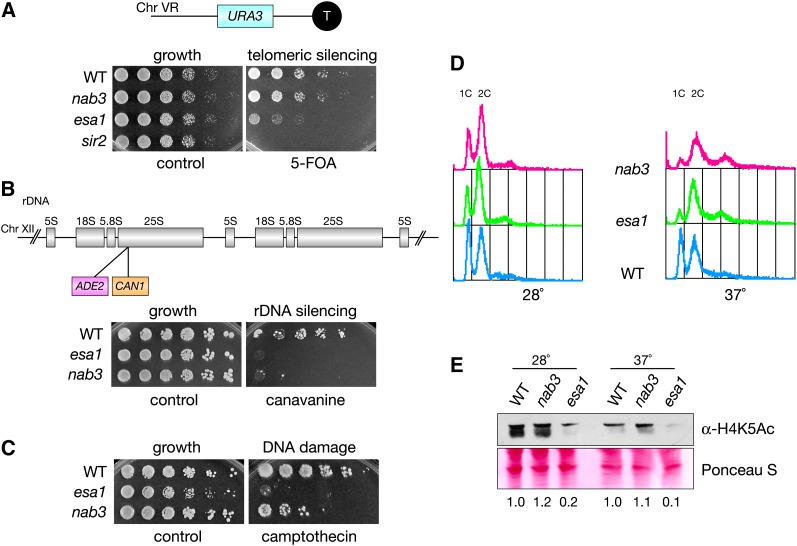
Figure 5 .
nab3 mutants display defects similar to esa1 mutants. (A) nab3 mutants display no defect in the telomeric 5-FOAS assay. WT (LPY4917), nab3-10 (LPY5407), esa1 (LPY4919), and sir2 (LPY4979) strains with a TELVR::URA3 reporter were plated on SC and 5-FOA. (B) nab3 mutants have an rDNA silencing defect. WT (LPY4909), esa1 (LPY4911), and nab3 (LPY5406) strains with the 25S rDNA::ADE2-CAN1 reporter were assayed for rDNA silencing defects on SC-Ade-Arg with and without 16 μg/ml canavanine. (C) The nab3 mutant is sensitive to the DNA-damaging agent camptothecin. WT (LPY5), esa1 (LPY4774), and nab3 (LPY10622) were plated on DMSO (control) and camptothecin (40 μg/ml) to test for drug sensitivity. (D) nab3 mutants display a G2/M block when grown at an elevated temperature. The same strains as in (C) were fixed and stained with propidium iodide to analyze cell-cycle profiles after being grown at 28° and shifted to 37° for 4 hr. (E) nab3 mutants have wild-type levels of global H4K5 acetylation. The same strains as in (C) and (D) were grown in YPD at 28° and shifted to 37° for 2 hr before whole-cell extract preparation. Samples were immunoblotted to detect global H4K5 acetylation levels. Compared with the H4K5 acetylation levels in esa1 mutants shown in Figure 3C, a more severe temperature challenge is shown here, accounting for the greater magnitude in decreased acetylation.