Figure 2. Effect of homologous substitutions on the fraction of functional sequences in a library of chimeric 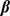 -lactamases.
-lactamases.
(A) The random field model agrees well with experimental data on random and homologous substitutions in  -lactamase [16]. The parabolic curve displays the effect of homologous substitutions, and the error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals of the fraction of correctly constructed chimeras (see Methods). The steep exponential curves (and inset) show the effect of random mutations, and the error bars represent one standard error. (B) As parent sequence identity decreases, the homologous substitution curves stretch to higher levels of mutation and lower fraction functional. Shown are the substitution curves for the
-lactamase [16]. The parabolic curve displays the effect of homologous substitutions, and the error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals of the fraction of correctly constructed chimeras (see Methods). The steep exponential curves (and inset) show the effect of random mutations, and the error bars represent one standard error. (B) As parent sequence identity decreases, the homologous substitution curves stretch to higher levels of mutation and lower fraction functional. Shown are the substitution curves for the  lac13 library (crossover locations and contacts) averaged over 100 random parent sequences with sequence identity ranging from 20–80%. (C) As the number of crossovers
lac13 library (crossover locations and contacts) averaged over 100 random parent sequences with sequence identity ranging from 20–80%. (C) As the number of crossovers  decreases, the homologous substitution curve shifts towards a higher fraction functional. Shown are the substitution curves for the
decreases, the homologous substitution curve shifts towards a higher fraction functional. Shown are the substitution curves for the 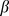 lac13 library (parents and contacts) averaged over 100 random crossover locations with the number of crossovers varying from 6 to 27. The random homologous substitution curve was generated by averaging over 100 randomly sampled sequences at each level of mutation.
lac13 library (parents and contacts) averaged over 100 random crossover locations with the number of crossovers varying from 6 to 27. The random homologous substitution curve was generated by averaging over 100 randomly sampled sequences at each level of mutation.
