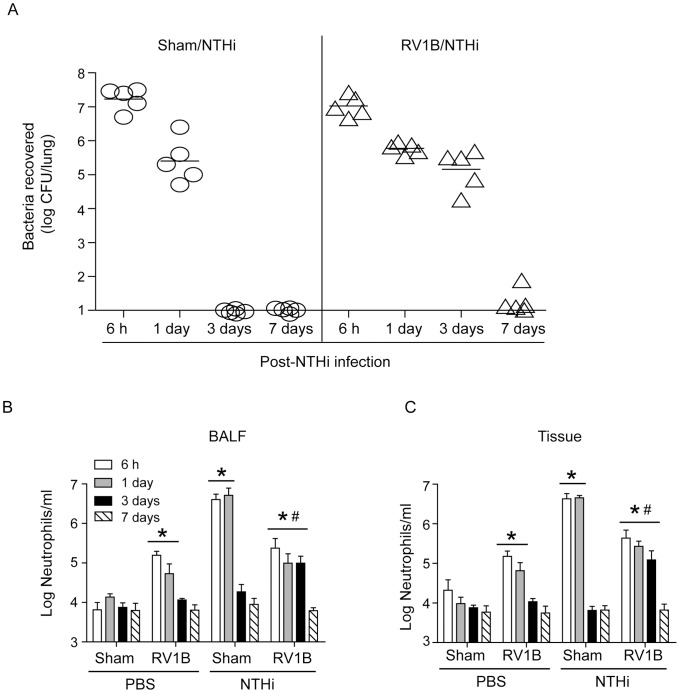
Figure 1. RV infection promotes bacterial persistence and decreases neutrophil infiltration to subsequent bacterial challenge in vivo.
BALB/C mice were infected with RV1B or sham by intranasal route. Two days later, mice were infected with NTHi or treated with PBS via intratracheal route and sacrificed at 6 h, 1 day, 3 days or 7 days post-NTHi infection. (A) Mice were sacrificed and lungs collected aseptically, homogenized in sterile PBS and 10 fold serial dilutions of lung homogenates were plated to determine bacterial density. (B) Cytospins of BAL cells and (C) lung digests enriched for leukocytes were prepared, stained with Diffquick and number of neutrophils were counted. Data in A represent mean and range and in B and C, mean±SD (n = 4–9, * p≤0.05, two-way ANOVA, different from sham; # p≤0.05, two-way ANOVA, different from sham/NTHi infected animals).