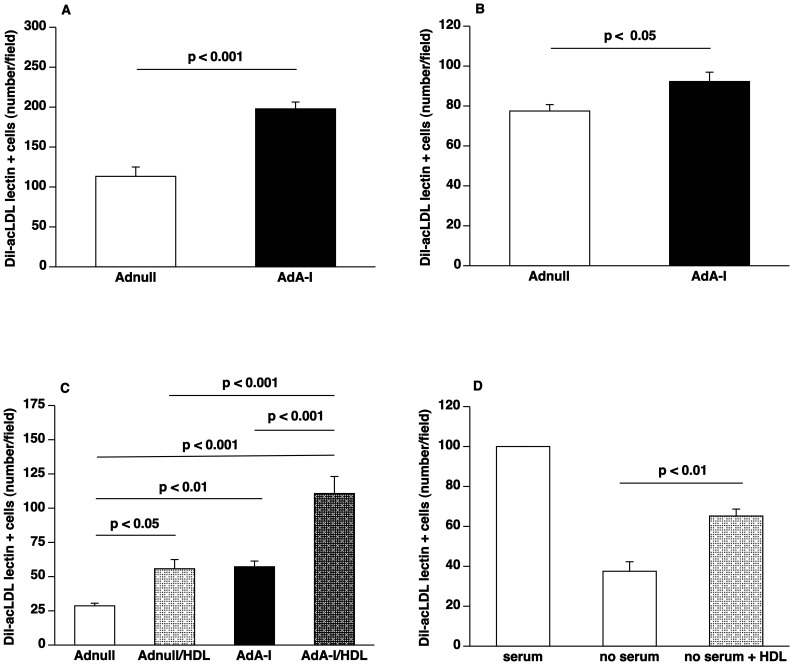
Figure 2. HDL raising gene transfer increases EPC number and enhances EPC function.
(A) Bar graph showing the number of Dil-acLDL FITC-isolectin double positive cells after 7 days of ex vivo culture of spleen mononuclear cells isolated at day 14 after Adnull transfer or AdA-I transfer in C57BL/6 LDLr−/− mice (n = 6 for each group). (B) Bar graph illustrating the number of Dil-acLDL FITC-isolectin double positive cells after 7 days of ex vivo culture of bone marrow mononuclear cells isolated at day 14 after Adnull transfer or AdA-I transfer in C57BL/6 LDLr−/− mice (n = 10 for each group). (C) Bar graph showing the number of migrated EPCs in modified Boyden chambers. After 7 days of culture, spleen EPCs isolated from Adnull injected mice (n = 5) or AdA-I treated mice (n = 6) were seeded in the upper chamber. The lower chamber was supplemented with either HDL (100 µg/ml) or an equivalent amount of bovine serum albumin and the number of migrated cells per microscopy field was quantified after 5 hours. (D) Bar graph illustrating the number of surviving murine EPCs. After 7 days of culture, spleen EPCs isolated from C57BL/6 LDLr−/− mice (n = 5) were cultured for 24 hours in EGM-2MV medium or medium without serum and growth factors either supplemented with HDL (100 µg/ml) or bovine serum albumin (100 µg/ml). The number of FITC-isolectin positive cells per microscopy field was quantified after 24 hours in a blinded fashion.