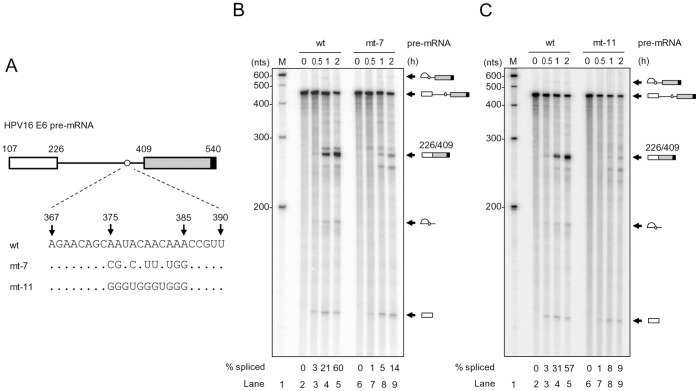
Figure 5. Introduction of point mutations into the mapped BPS in HPV16 intron 1 inhibits RNA splicing in vitro.
(A) Diagram of HPV16 pre-mRNA used in in vitro splicing assays. First exon (nt 107–226) and second exon (nt 409–540), indicated by white and gray rectangles, respectively, are separated by its native intron 1 containing a wt, mt-7 or mt-11 BPS. An 11-nt U1 binding site (black rectangle) attached to each RNA 3′ end served as a 5′ ss or splicing enhancer to promote in vitro RNA splicing. (B and C) Reduction of HPV16 RNA splicing in vitro by introduction of point mutations into the mapped BPS. In vitro RNA splicing assay was performed with 32P-labeled HPV16 E6 pre-mRNA in the presence of HeLa nuclear extract at 30°C for the indicated splicing reaction time (h). Spliced products were resolved in a 6% denaturing PAGE gel and their identities are shown on the right. Splicing efficiency (% spliced) was calculated as described [24] from each spliced gel and is shown at the bottom of the gel.