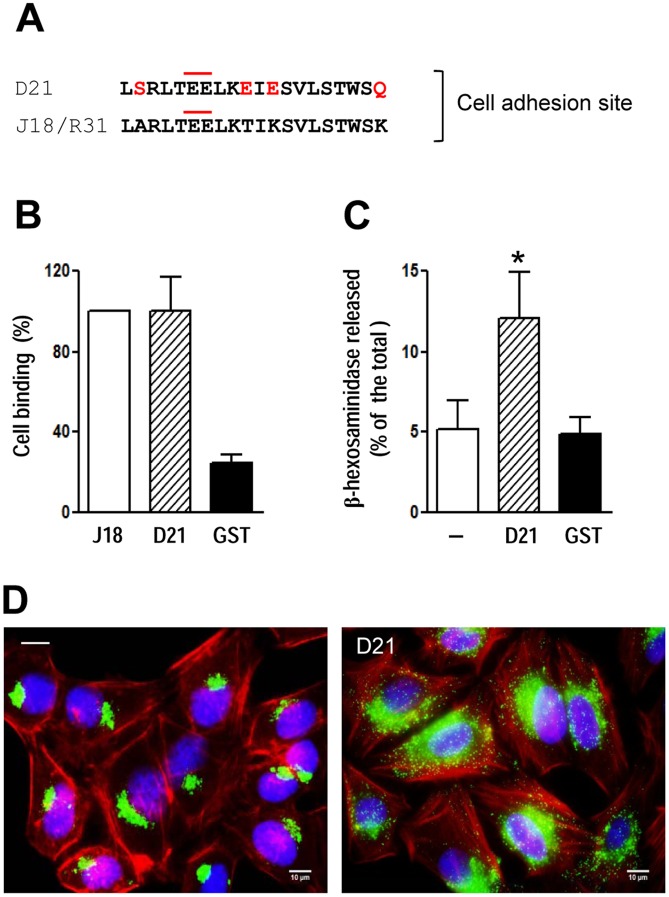
Figure 3. Binding of the recombinant protein D21 to HeLa cells and induction of lysosomal exocytosis.
A) D21 sequence was aligned to the J18 sequence previously identified as the host cell binding site, with the changed residues highlighted in red. The pair of contiguous glutamic acid residues implicated in cell binding is marked by an upper red line. B) HeLa cells were incubated with the indicated proteins, at 20 µg/ml, and the binding assay proceeded as described in the methods section. GST was used as control. Values, given relative to the binding of J18, which were fixed to 100, are the means ± SD of three independent assays performed in duplicate. C) Semi-confluent HeLa cell monolayers were incubated in absence or in the presence of D21 at 20 µg/ml. After 1 h, the supernatants were collected and the release of β-hexosaminidase was measured. Exocytosis was expressed as percentage of total β-hexosaminidase activity (supernatant+cell extract). The values are the means ± SD of three independent assays. The intensity of exocytosis was significantly higher in the presence of D21 (*p<0.05). GST had no effect. D) Hela cells were incubated for 1 h in absence or in the presence of D21, and then processed for immunofluorescence using anti-Lamp-2 antibody and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (green), phalloidin-TRITC (red) for actin visualization and DAPI (blue) for DNA.