Figure 7. Anatomy of ferret auditory cortex.
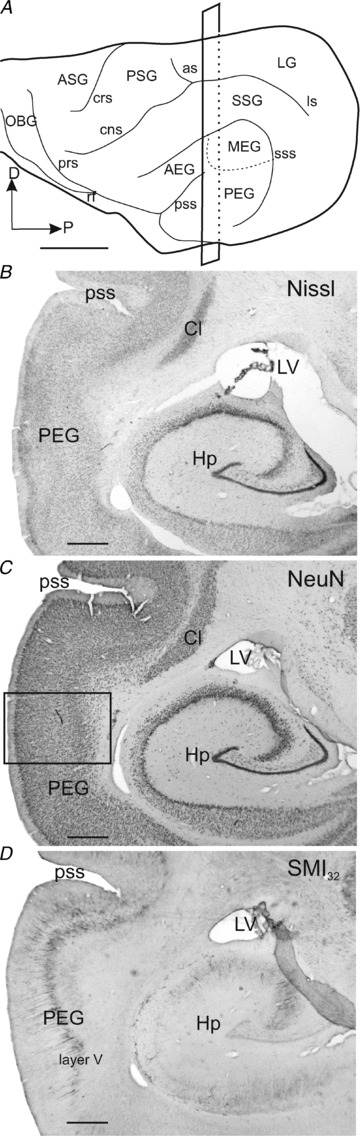
A, lateral view of the ferret cortex showing the ectosylvian gyrus where the auditory cortex is located and its three main regions. B–D, consecutive coronal sections were stained for three different neuronal markers, Nissl substance (B), NeuN (C) and SMI32 (D). The rectangle in A shows the cutting plane at the level of the photomicrographs in B–D. The rectangle in C indicates where the higher magnification image shown in Fig. 8C was taken. Scale bars, 5 mm in A and 1 mm in B–D. AEG, anterior ectosylvian gyrus; ASG, anterior sigmoid gyrus; as, ansinate sulcus; Cl, claustrum; cns, coronal sulcus; crs, cruciate sulcus; D, dorsal; Hp, hippocampus; LG, lateral gyrus; ls, lateral sulcus; LV, lateral ventricle; MEG, middle ectosylvian gyrus; NeuN, neuronal nuclei protein antibody; OBG, orbital gyrus; P, posterior; PEG, posterior ectosylvian gyrus; prs, presylvian sulcus; PSG, posterior sigmoid gyrus; pss, pseudosylvian sulcus; rf, rhinal fissure; SMI32, Neurofilament H non-phosphorylated; SSG, suprasylvian gyrus; sss, suprasylvian sulcus.
