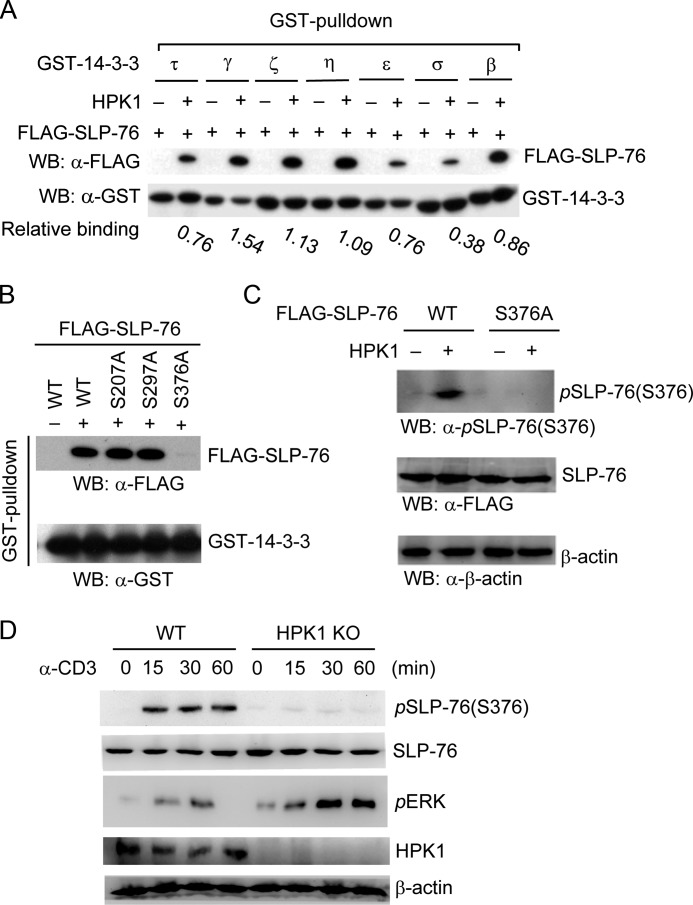
FIGURE 1.
HPK1-induced SLP-76 Ser-376 phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding. A, interaction of SLP-76 with different 14-3-3 isoforms in the presence of HPK1. FLAG-SLP-76 was transfected into HEK293T cells with HPK1. The interaction of SLP-76 with 14-3-3 isoforms was detected by GST pulldown assays using GST-14-3-3 proteins. The relative binding of SLP-76 to 14-3-3 isoforms was calculated by the amount of GST-14-3-3-bound SLP-76 divided by the amount of GST-14-3-3 input as determined by densitometry analyses. WB, Western blot. B, the S376A mutation abolishes HPK1-dependent SLP-76/14-3-3 interaction in vitro. The serine residues located in the potential 14-3-3-binding sites (e.g. Ser-207, Ser-297, and Ser-376) within SLP-76 were individually mutated to alanine. WT SLP-76 and mutants were transfected into HEK293T cells with HPK1. The cell lysates were subjected to GST-14-3-3τ pulldown assays, followed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG antibody. GST-14-3-3 input was detected by Western blotting with anti-GST antibody. C, Ser-376 of SLP-76 is phosphorylated by HPK1 in HEK293T cells. HPK1 was cotransfected with either FLAG-SLP-76 (WT or S376A mutant) into HEK293T cells. The cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with anti-phospho-SLP-76 (Ser-376) antibody. The protein levels of WT SLP-76 and the S376A mutant were detected by anti-FLAG antibody. D, induction of SLP-76 Ser-376 phosphorylation in WT (but not HPK1-deficient) T cells during TCR signaling. Splenic T cells were isolated from WT and HPK1-deficient mice and stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody for the indicated time periods, followed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-SLP-76 (Ser-376) antibody. ERK phosphorylation was determined as a control. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. KO, knock-out.