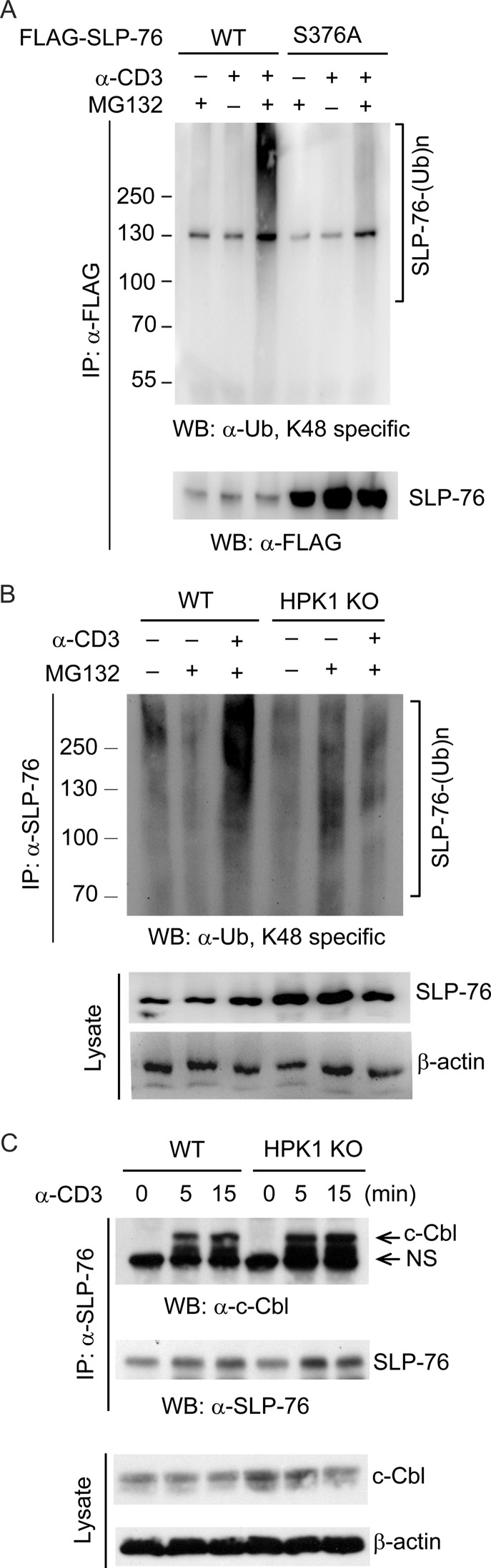
FIGURE 4.
HPK1 induces SLP-76 ubiquitination during TCR signaling. A, SLP-76 Ser-376 phosphorylation mediates SLP-76 ubiquitination during TCR signaling. Jurkat TAg cells were transfected with FLAG-SLP-76 (WT or S376A mutant), pretreated with or without MG132 for 3 h, and stimulated by anti-CD3 antibody for 15 min. SLP-76 was immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-FLAG antibody, followed by Western blotting (WB) with anti-ubiquitin (α-Ub; Lys-48) antibody. B, HPK1 deficiency suppresses SLP-76 ubiquitination in primary murine T cells upon anti-CD3 stimulation. Murine splenic T cells from WT and HPK1-deficient mice were pretreated with MG132 for 4 h and then stimulated with anti-CD3 antibody for 30 min. SLP-76 was immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates using anti-SLP-76 antibody, followed by Western blotting with anti-ubiquitin (Lys-48) antibody. SLP-76 and β-actin in the lysates were detected as controls. KO, knock-out. C, HPK1 deficiency does not affect c-Cbl/SLP-76 interaction in T cells upon TCR signaling. SLP-76 was co-immunoprecipitated from unstimulated and anti-CD3 antibody-stimulated T cells using anti-SLP-76 antibody, followed by Western blotting with anti-c-Cbl antibody. Data are representative of three independent experiments.