FIGURE 1.
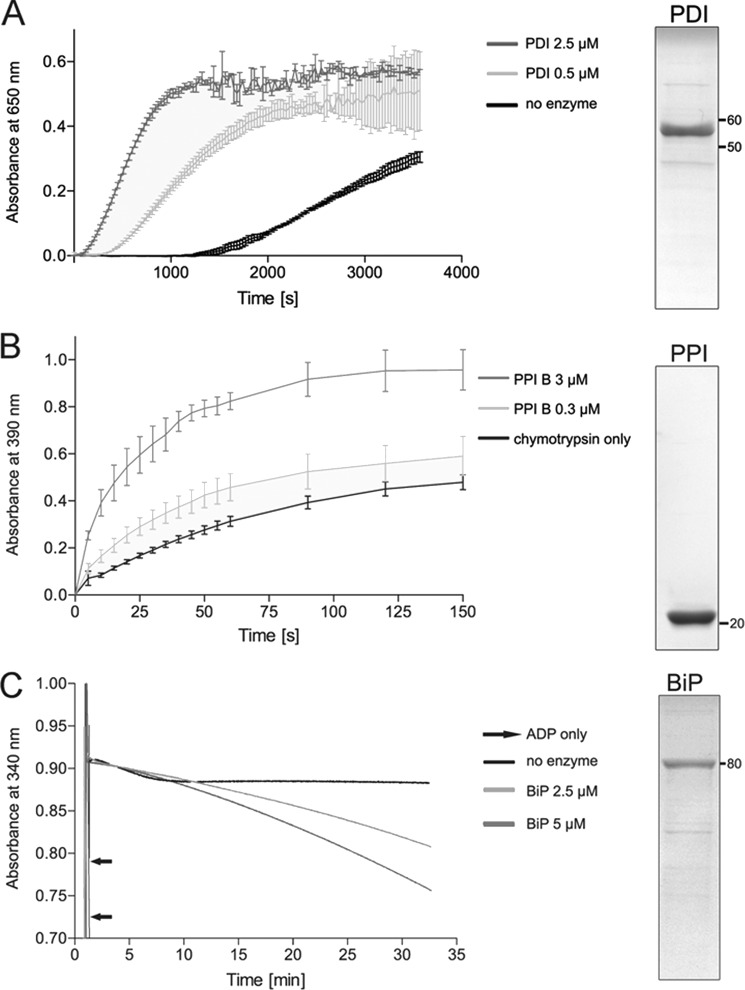
Purity and integrity of recombinant Conus enzymes as determined by SDS-PAGE and enzyme-specific activity assays. The purity of recombinant enzymes was determined by SDS-PAGE (right panels). A total of 3 μg of recombinant protein was separated on 12% Tris-glycine gels under reducing conditions. Proteins were visualized by Coomassie staining. A, PDI activity was measured using the insulin reductase assay. The addition of PDI (0.5 and 2.5 μm) caused rapid reduction of insulin, as observed by an increase in absorbance at 650 nm. This effect was concentration-dependent. B, the cis-trans isomerase activity of PPI B was measured using the coupled chymotrypsin assay. The addition of PPI B (0.3 or 3 μm) resulted in an increase in the rate of cis-trans isomerization of the oligopeptide N-succinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-p-nitroanilide, a substrate of chymotrypsin (mean ± S.D.). Enzymatic cleavage leads to liberation of p-nitroanilide and an increase in absorbance at 390 nm. This reaction was concentration-dependent. C, the ATPase activity of BiP was determined using the NADH-coupled photometric assay. Hydrolysis of ATP was followed by monitoring depletion of NADH at 340 nm. The addition of ADP led to a sudden decrease in absorbance, confirming the functionality of the assay. In the presence of BiP (2.5 and 5 μm), absorbance slowly decreased over the time course of the assay, whereas no effect was observed for the no enzyme control. This effect was concentration-dependent.