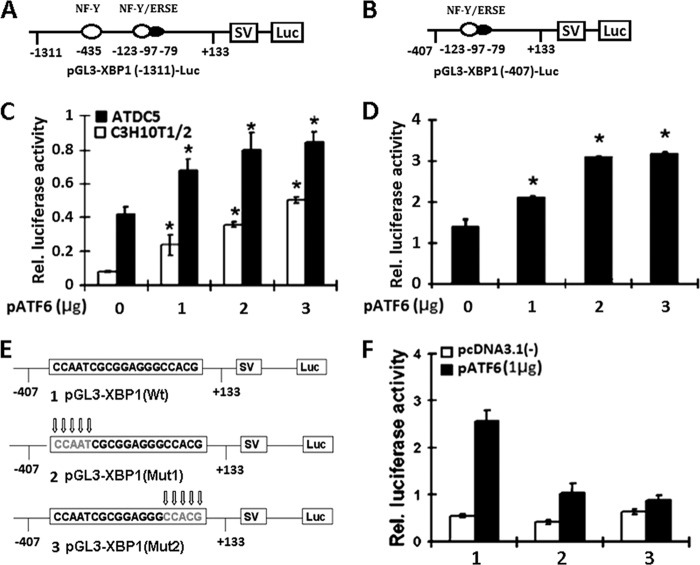
FIGURE 4.
ATF6 activates the transactivation of pXBP1 reporter genes. A and B, schematic structures of two XBP1-specific reporter genes. The indicated segments from the 5′-flanking region of the XBP1 gene were linked to an SV40 promoter (SV) and a DNA segment encoding luciferase (Luc). Black ovals, the ERSE elements that are ATF6-binding elements; numbers, distances in nucleotides from the first nucleotide of intron 1. C, ATF6 activates the longer pXBP1-specific reporter construct pGL3-XBP1 in both C3H10T1/2 pluripotent cells and ATDC5 chondrocytes. The reporter gene and the pCMV-gal internal control plasmid were transfected into cells together with the pcDNA3.1(−)-ATF6 expression plasmid. At 48 h after transfection, the cultures were harvested, and the luciferase and β-galactosidase activities were determined. The data shown are the mean levels of luciferase activity from three independent experiments, analyzed in triplicate and normalized by β-gal activity. *, p < 0.05. D, ATF6 activates the XBP1 promoter core sequence reporter construct pGL3-XBP1 in C3H10T1/2 cells. The same procedure as described in C was followed. E, diagrams show the alterations in the ATF6-binding sites in the pGL3-XBP1 reporter gene. Mutant nucleotides are indicated by arrows. F, ATF6-dependent transactivation of the XBP1 gene was dramatically reduced when the ATF6-binding site was mutated. The wild type or mutant reporter gene specified and the pCMV-gal internal control plasmid were transfected into ATDC5 cells together with a pcDNA3.1(−) vector (control) or a pATF6 expression plasmid, and the same procedure as described in C was followed. 1, pGL3-XBP1(Wt); 2, pGL3-XBP1(mut1); 3, pGL3-XBP1(mut2). Error bars, S.D.