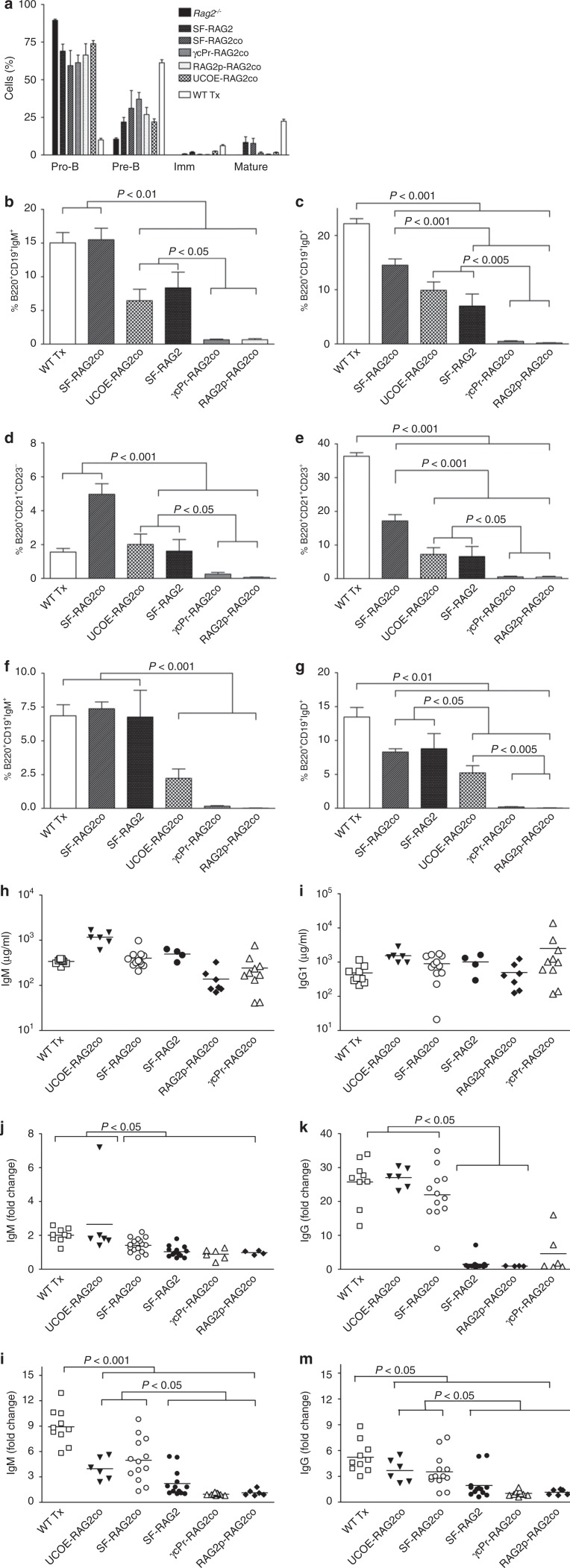
Figure 4.
Bone marrow B lymphocyte maturation populations in spleen and lymph nodes. (a) Bone marrow B-cell differentiation was assessed within B220+ gated cells for pro-B (B220+CD43+IgM−IgD−), pre-B (B220+CD43−IgM−IgD−), immature (Imm; B220+CD43−IgM+IgD−) and mature (B220+CD43−IgM+IgD+) cells (n = 4–9). (b,c)Spleen B-cell percentages of B220+CD19+IgM+ and B220+CD19+IgD+, and (d) specification into CD21+CD23+ follicular B cells and (e) CD21+CD23− marginal zone B cells and (f,g) B-lymphocytes in the lymph nodes. Normalization of the immunoglobulin plasma levels determined for (h) IgM and (i) IgG1 as well as isotypes IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG3, IgA, which are presented in Supplementary Figure S4 (n = 4–10) occurs in the gene therapy treated mice, 4 months after transplantation of transduced Lin- cells. Rag2−/− mice do not have detectable Ig levels (data not shown). Four months after transplantation, T cell dependent specific (j) IgM and (k) IgG responses to antigen were determined by tetanus toxoid administration. Tetanus toxoid was three times injected intraperitoneally at two week intervals, and blood was collected before every injection and two weeks after the last injection. IgM was determined at day 14 after the first injection, IgG at 14 days after the last injection. Shown are the fold changes in optical density relative to pre-immunization values. Furthermore, T-cell independent immune response was induced by Pneumo23, and fold changes are presented for (l) IgM and (m) IgG at day 10 after immunization.