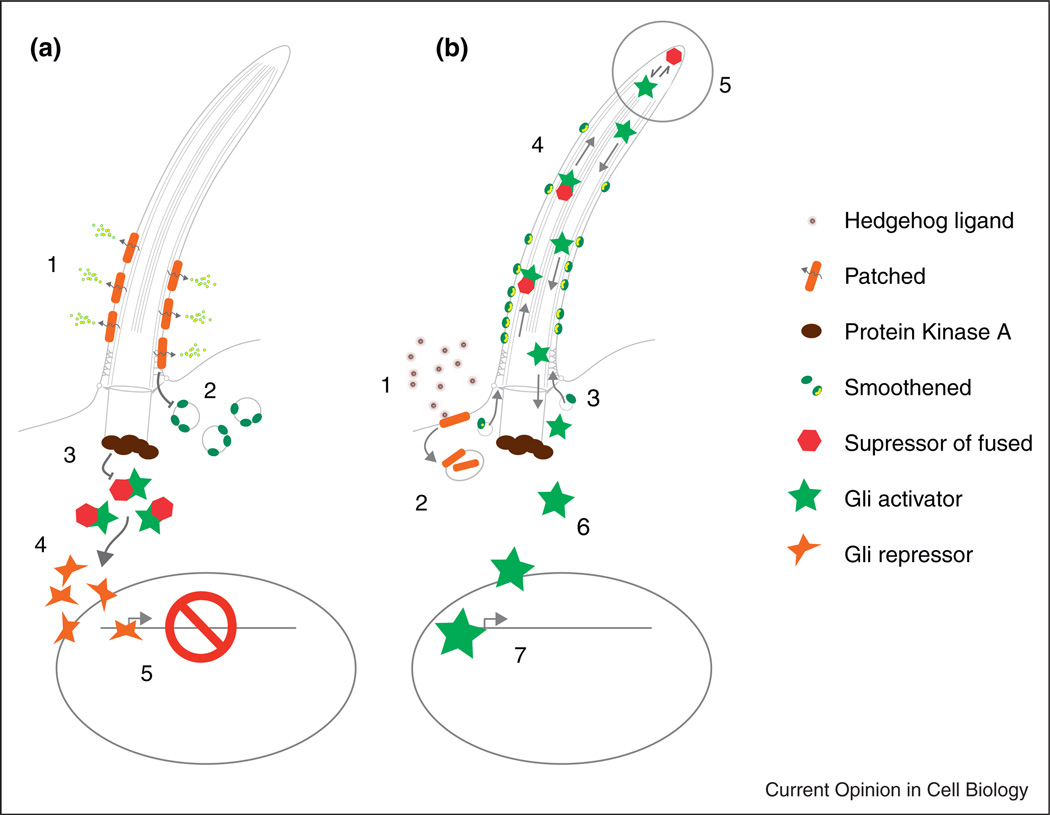
Figure 1.
Recent advances in cilia-mediated Hedgehog signaling. For a complete overview of Hh signaling see Ref. [11]. (a) Resting cell state with Hh signaling inhibited. The Hedgehog receptor Patched acts as a sterol efflux transporter on the cilia membrane, restricting the amount of Smoothened seven transmembrane protein present on the cilium (2). Protein kinase A activity prevents access of Sufu:Gli complexes (3) to the cilium. Cytoplasmic processing of Gli to the Gli repressor form (4) and transit to the nucleus maintains Hh target genes in a repressed state (5). (b) Activation of Hh signaling in cilia by Hh ligand binding. (1) Hedgehog ligand binds Patched (1), promoting removal from the membrane and blocking its sterol efflux function (2). Sterol bound Smoothened accumulates in the cilia membrane (3), abrogates PKA inhibition of Sufu:Gli complex entry into the cilium, allowing transport of Sufu:Gli complexes to the cilia tip (4). Cilia tip accumulation of Sufu:Gli promotes dissociation of full-length activator Gli proteins by undefined mechanisms (5), allowing Gli activator egress from the cilia (6), transit to the nucleus (7) and activation of Hh target genes.