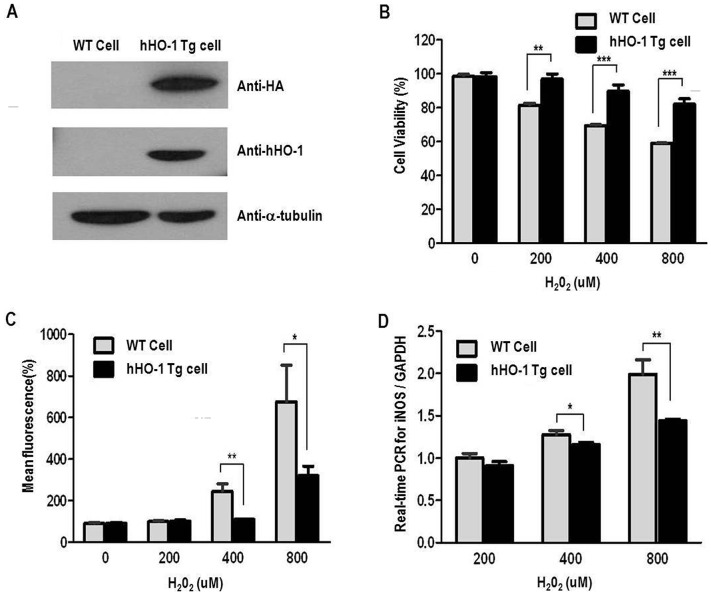
Figure 4. Anti-oxidant effects of fibroblasts from the hHO-1-Tg pig.
A: Western blot analysis for hHO-1 and HA in the hHO-1-Tg fibroblasts using anti-HO-1 (1∶200) and anti-HA (1∶4,000) antibodies. The α-tubulin was used as a control. B: Cell viability was higher in the hHO-1-Tg fibroblasts compared to the wild-type. After H2O2 (0, 200, 400 or 800 µM) treatment, cell viability was slightly better in the hHO-1-Tg fibroblast than in the wild-type fibroblasts. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8 after induction with H2O2 for an additional 1 hr. C: Level of ROS was significantly reduced in the hHO-1-Tg fibroblasts in comparison to the wild type fibroblasts. After H2O2 treatment, ROS production was significantly reduced in the hHO-1-Tg fibroblasts compared with the wild-type fibroblasts. Fibroblasts obtained from ear tissues were incubated with 25 µM DCFH-DA for 15 minutes at 37°C, and ROS were measured using FACS. D: Expression of the iNOS gene by real-time PCR in hHO-1-Tg fibroblasts compared with the wild-type fibroblasts. The threshold cycle (Ct) value was defined as the number of PCR cycles at which the fluorescence crossed a fixed threshold above baseline. For relative quantification, the ΔΔCt method was used to measure fold changes of cDNA. (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001).