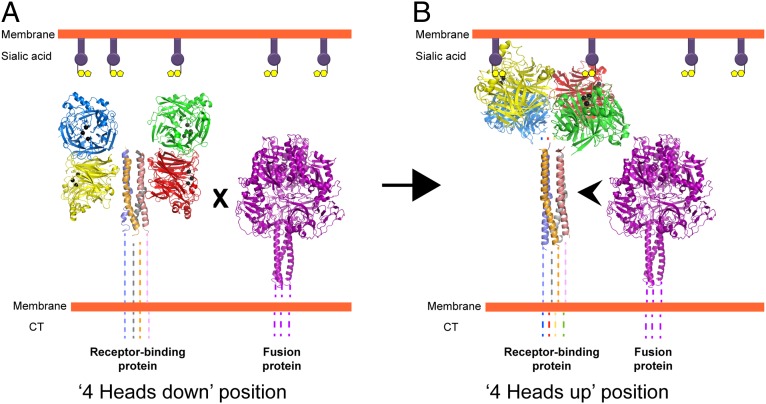
Fig. 7.
Schematic model of paramyxovirus F activation based on putative structural rearrangements in the receptor-binding protein. (A) The receptor-binding protein in the four-heads-down position. The formation of the contacts in the head–stalk interface prevents physical interaction of F with the stalk region of the receptor-binding protein. (B) Creation of the contacts in the dimer-of-dimer interface of the receptor-binding protein in the four-heads-up position moves the heads upwards, exposing the stalk. This exposure allows F to interact with the HN stalk, causing F triggering. Black balls indicate the sialic acid binding site residues in the four neuraminidase head domains (colored red, green, blue, and yellow) of paramyxovirus HN. Prefusion F is represented by the PIV5 prefusion F structure (purple) (6). Dotted lines represent regions of paramyxovirus F and HN proteins for which no structural data are available. CT, cytoplasmic tail.