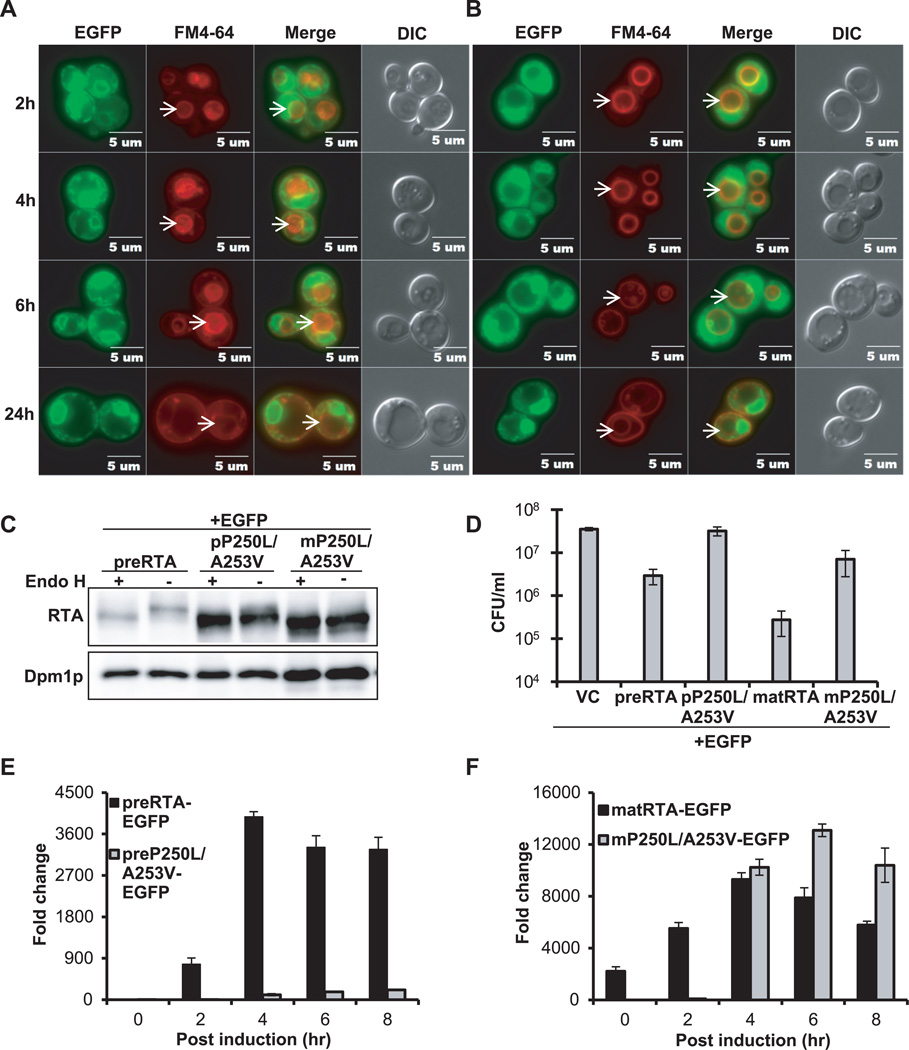
Figure 5. Intracellular transport, protein expression, cytotoxicity and depurination activity of preP250L/A253V-EGFP and mature P250L/A253V-EGFP.
(A) Trafficking of preP250L/A253V-EGFP and (B) matP250L/A253V-EGFP in yeast. The images were taken at 2, 4, 6 and 24 hpi with Olympus BX41 fluorescence microscope. Merged images show localization of each protein relative to the vacuole. The arrows indicate the vacuoles. (C) Immunoblot analysis of membrane fraction isolated from cells expressing each protein at 6 hpi were treated with (+) or without (−) Endo H to cleave the glycans. The proteins (5 µg) were separated on a 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and probed with monoclonal anti-RTA (1:5000). The blot was reprobed with the ER membrane marker Dpm1p as a loading control. (D) Viability of yeast expressing each protein and the vector control (VC). (E) Ribosome depurination by preP250L/A253V-EGFP and preRTA-EGFP by qRT-PCR. (F) Ribosome depurination by matP250L/A253V-EGFP and matRTA-EGFP by qRT-PCR. Data are mean ± SD from triplicates.