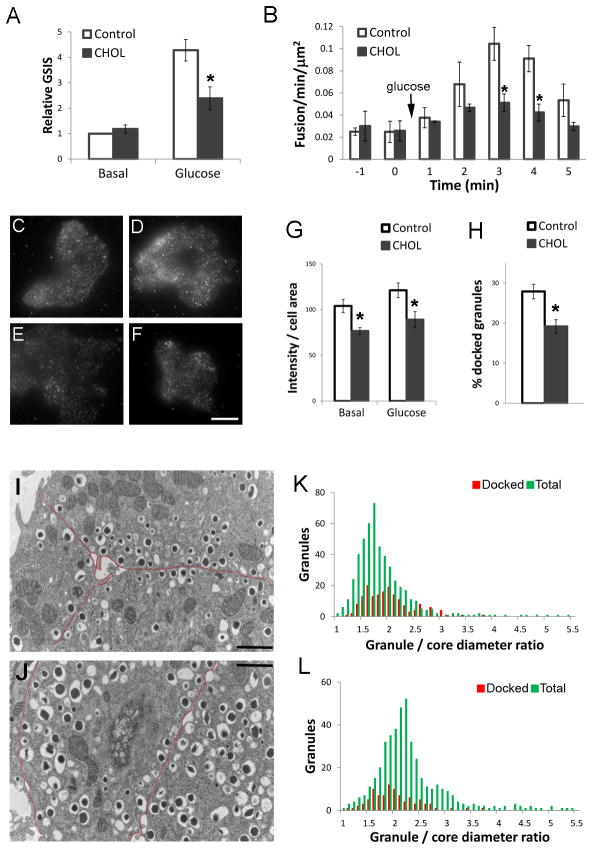
Figure 9.
Excess cholesterol accumulation impairs insulin granule docking and fusion. For all experiments, 20 mM glucose was used for stimulation. (A) Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) was measured in control and CHOL INS1 cells. Basal secretion in control cells was set to 1. n=4. (B) Glucose-stimulated fusion events were measured by TIRFM in control and CHOL INS1 cells transfected with VAMP2-pHluorin. n=548 events from 7 cells. (C–G) Basal (C,E) and glucose-stimulated (15 min, D, F) control (C, D) and CHOL (E, F) MIN6 cells were fixed and stained with insulin antibody and imaged by TIRFM. Bar, 10 μm. (G) Quantification of background corrected fluorescence intensity normalized to cell area from experiments shown in (C–G). n=40 cells. (H–L) MIN6 cells or isolated islets cultured in 11 mM glucose were used. Granules having centers within 200 nm of the plasma membrane were defined as docked. (H) Fraction of docked granules in TEM images of control and CHOL MIN6 cells. n=34 cells. (I–L) TEM of control (I, K) and CHOL (J, L) mouse islets with the plasma membrane marked by red lines in (I, J). Bar, 1 μm. (K, L) Distribution profiles of docked (red) vs. total (green) granules. n=941 from 18 images. All panels, data are mean ± SEM; *, p<0.05 by student t-test against control cells.