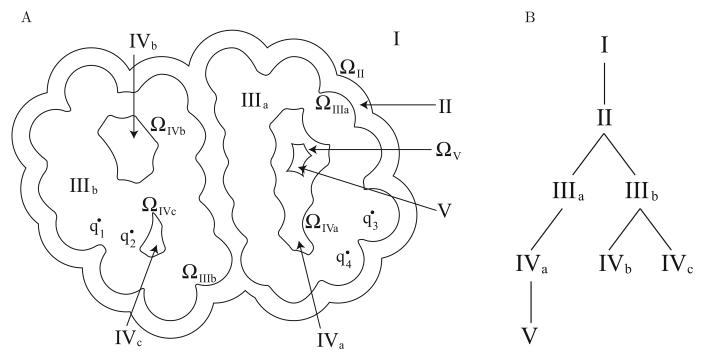
Figure 4.
Tree representation of a general surface problem. The example molecular geometry shown in (A) might correspond to an encounter complex between two associating proteins (Regions IIIa and IIIb) with point charges qi, surrounded by a single ion-exclusion layer (Region II), which in turn is surrounded by solvent with salt (Region I). The binding partners contain several solvent filled cavities (Regions IVa–c), and one cavity is large enough to contain a small ion-exclusion layer (Region V). The tree representation for this example multi-surface geometry is shown in (B).