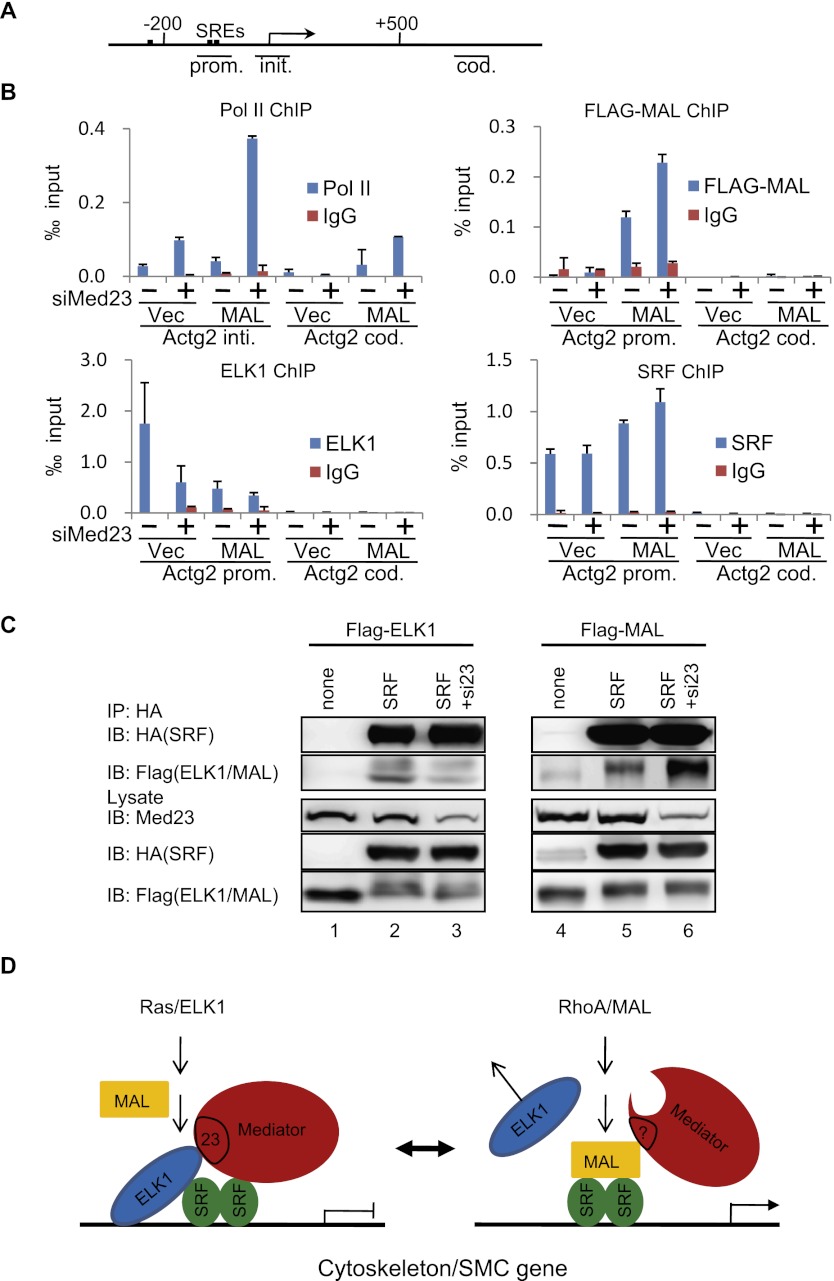
Figure 6.
MED23 modulates the regulator occupancy at the SMC genes. (A) SRF-binding sites. The line below shows the Actg2 gene region amplified in ChIP. (B) ChIP experiments were performed in Ctrl, siMed23, oxMal, and siMed23+oxMal 10T1/2 cells using antibodies against Pol II, Flag, SRF, and ELK1; IgG was used as a negative control. The precipitated DNA was analyzed by real-time PCR with primers targeting the Actg2 transcriptional initiation region (Actg2 init.), promoter region (Actg2 prom.), and coding region (Actg2 cod.). The relative binding level of each factor was calculated by normalization to the input DNA. The average of three separate experiments is shown, and the standard deviation is indicated. (C) Co-IP of SRF with ELK1 (left panel) or MAL (right panel) in siCtrl and siMed23 HeLa cells. Flag-ELK1 (or Flag-MAL) plasmid was transfected into HeLa cells with or without HA-SRF. Whole-cell extracts were analyzed directly (lysate) or following immunoprecipitation with anti-HA antibody (IP: HA). (D) A schematic model for Mediator MED23 in regulating the complex formation of SRF/ELK1 versus SRF/MAL.