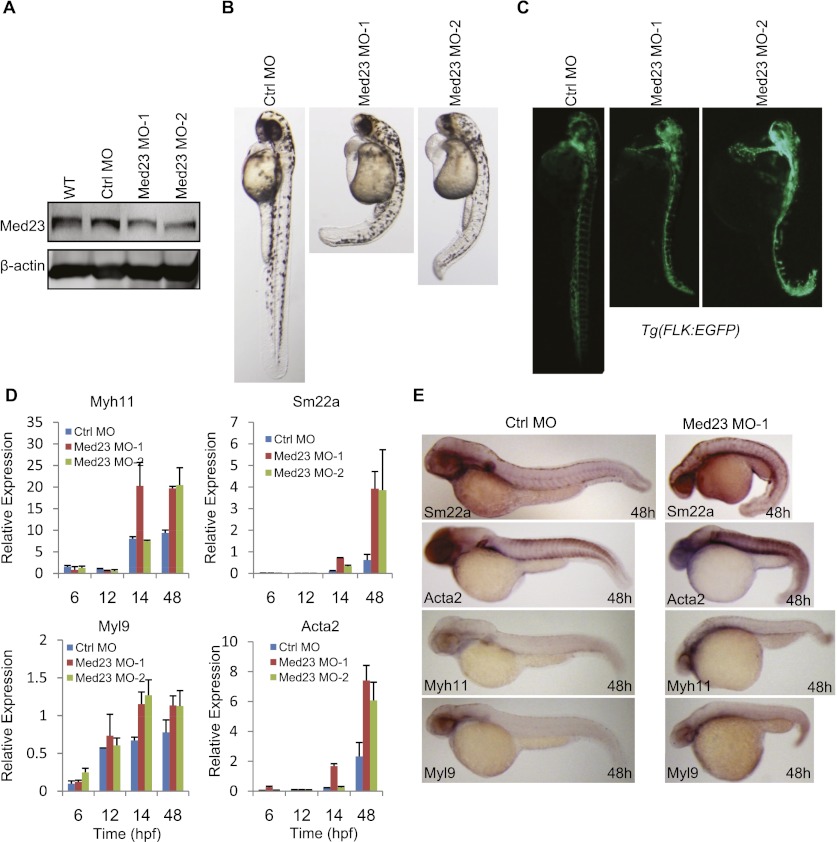
Figure 7.
Med23 deficiency promotes smooth muscle development in zebrafish. (A) Western blot analysis of MED23 knockdown efficiency. Embryos without injection (wild-type [WT], lane 1), injected with 4 ng of Ctrl MO (lane 2), 4 ng of Med23 MO-1 (lane 3), or 2 ng of Med23 MO-2 (lane 4) were harvested at 24 hpf. Protein samples were prepared, subjected to SDS-PAGE, and blotted with antibody against Med23. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Phenotypic analysis of zebrafish embryos at 48 hpf. Embryos injected with Ctrl MO, Med23 MO-1, or Med23 MO-2 were analyzed. Embryos are lateral views with anterior to the top. (C) Embryos derived from the transgenic zebrafish line Tg(flk:EGFP) were injected with the two Med23 MOs and showed significant increased fluorescent intensity. Embryos are lateral views with anterior to the top. (D) Real-time PCR analysis of SMC markers (Acta2, Sm22a, Myh11, and Myl9) at the indicated time points. (E) Whole-mount in situ hybridization for embryos injected with Ctrl MO and Med23 MO-1 was performed at 48 hpf. Riboprobes to SMC markers (Sm22a, Acta2, Myh11, and Myl9) were used. All embryos are lateral views with anterior to the left.