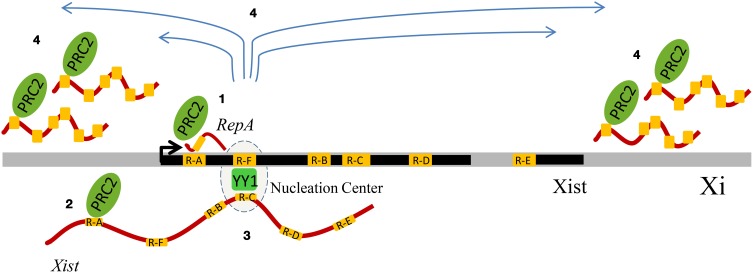
Figure 2.
Schematic summary of the influence of genomic repeats on X-chromosome inactivation (XCI). The Xist DNA locus displays tandem repeats (visualized in yellow) and generates multiple transcripts (such as RepA and Xist), whose contribution to XCI involves binding to Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) and YY1, which has also been associated to Polycomb. Four sequential events of XCI are represented. During the initiation phase of XCI, the Repeat A (R-A) region of the ncRNA RepA recruits PRC2, creating the conditions for the production of the full-length Xist RNA (1). Xist co-transcriptionally binds PRC2 via its R-A region, and it is loaded onto chromatin (2). YY1 functions as a bridge and anchors Xist in cis, by binding both Xist RNA and DNA, respectively via their Repeat C (R-C) and Repeat F (R-F) regions (3). Xist RNA, first bound only on the nucleation center, spreads in cis and recruits PRC2, thus mediating the X-chromosome inactivation (4).