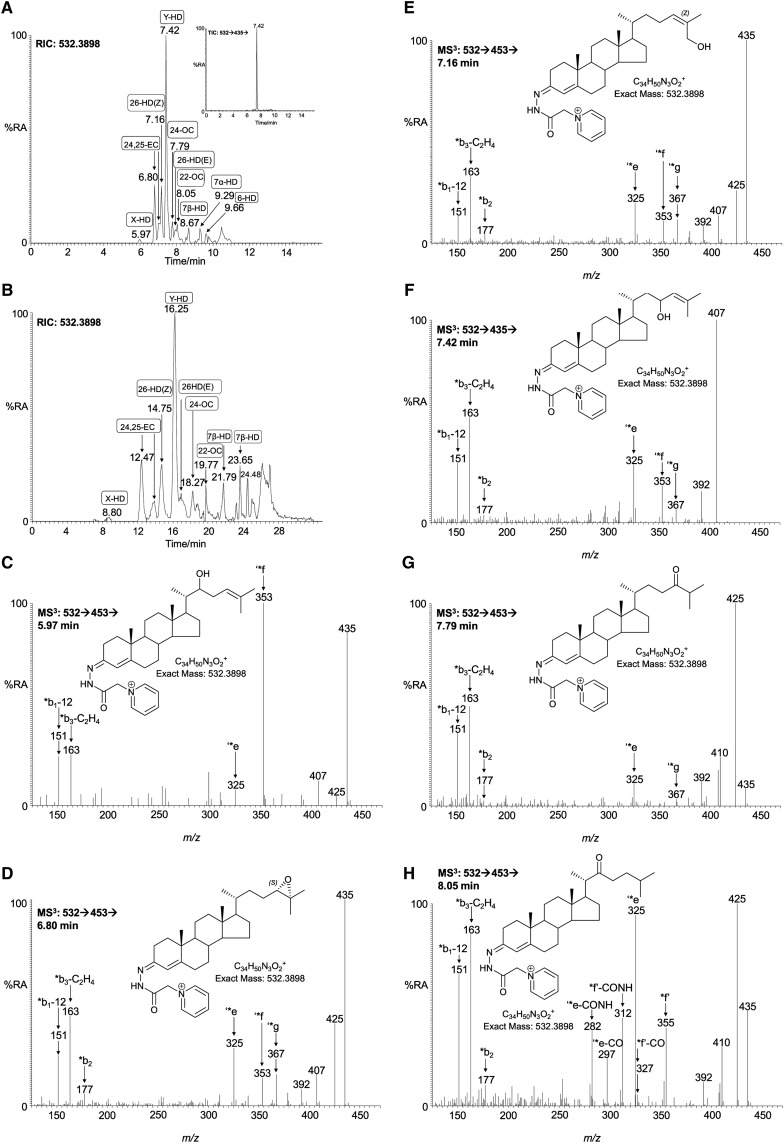
Fig. 3.
Oxo and epoxycholesterols and hydroxydesmosterols in newborn mouse brain. RIC of m/z 532.3898 ± 10 ppm acquired using the short (A) and long (B) gradient. The inset in A shows the TIC for the [M]+→[M-97]+→ transition. C–E, G–H: MS3 ([M]+→[M-79]+→), and F: [M]+→[M-97]+→ spectra are assigned to GP-tagged oxysterols. C: X-hydroxydesmosterol (X-HD); D: 24S,25-epoxycholesterol (24,25-EC); E: (24Z),26-hydroxydesmosterol [cholesta-5,24Z-diene-3β,26-diol, 26-HD(24Z)]; F: Y-hydroxydesmosterol (Y-HD); G: 24-oxocholesterol (24-OC); H: 22-oxocholesterol (22-OC). Assignments are based on a comparison of retention time, exact mass, and MSn spectra with, where possible, those of authentic standards. Authentic standards were available for 24S,25-epoxycholesterol, (24Z),26-hydroxydesmosterol, (24E),26-hydroxydesmosterol, 24-oxocholesterol, and 22-oxocholesterol. X and Y correspond to locations of hydroxy groups on the C-17 side-chain, probably at C-22 and -23, respectively.