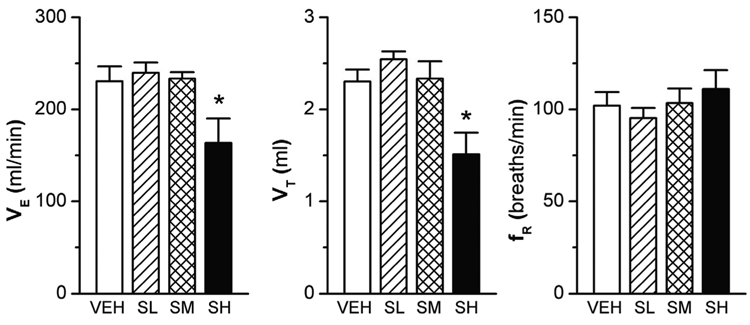
Figure 2.
Baseline ventilation (VE) in the surviving conscious rats 2 h after sarin exposure. The baseline VE, as compared with that in the vehicle (VEH)-exposed rats, was not changed by low and moderate levels of sarin (SL and SM), but was significantly reduced by high-level sarin (SH) due to a reduction of tidal volume (VT) with little effect on respiratory frequency (fR). Mean ± SE; n = 12, 12, 8, and 8 for VEH, SL, SM, and SH animals, respectively. * P < 0.01, SH vs. three other groups.