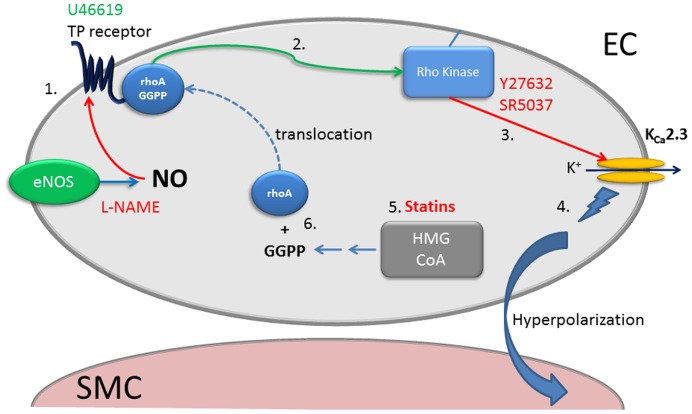
Figure 7. Schematic diagram showing potential regulatory mechanisms of KCa2.3 channels by TP receptor/rho mediated signalling.
Increased stimulation of the TP receptor with the agonist U46619 or following inhibition of NOS (eNOS) with L-NAME (NO can supress the action of TP receptors or synthesis of metabolites that activate TP) (1) results in activation of rhoA and stimulation of Rho kinase (2). Rho kinase (or associated signalling) inhibits KCa2.3 function (3) and inhibitors of Rho kinase (Y27632 or SR5037) restore or protect the KCa2.3 component of EDH (4). Statins by inhibiting HMG-CoA prevent formation of the isoprenoid GGPP (5). This reduces Rho mediated signalling by preventing GGPP dependent translocation of rhoA to the plasma membrane (6). Therefore statins protect KCa2.3 function by inhibiting Rho-mediated signalling via the TP receptor (1–3.). Red arrows/text indicates an inhibitory mechanism. Green text/arrows represent a stimulatory mechanism. Blue arrows indicate synthetic pathways; dashed blue line indicates translocation to the plasma membrane.