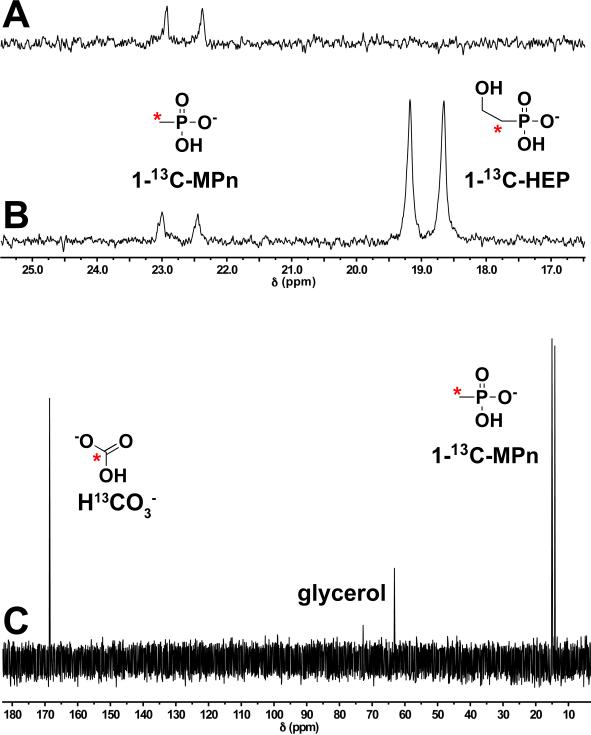
Fig. 1.
In vitro assay of MpnS activity. (A) Crude cell extract from an E. coli MpnS overexpression strain was incubated aerobically with 1-13C-HEP in the presence of Fe(II) and the phosphorus-containing products were examined using 31P NMR spectroscopy. After incubation for 1 hour a single product was observed as a doublet centered at 23.5 ppm. The mass and retention time of this product determined by LC-MS is consistent with this product being 1-13CMPn (Fig. S3). (B) Spiking of this reaction with the substrate, 1-13C-HEP produced a second doublet centered at 19 ppm, showing that the substrate was completely consumed in the initial reaction. (C) The identity of the reaction products was determined using 13C NMR after repeating the assay in a sealed vial using purified MpnS with a mixture of 1-13C-HEP and 2-13C-HEP as substrates. The C-2 labeled carbon of HEP is converted to 13C bicarbonate (H13CO -3), while the C-1-labelled carbon is converted to 1-13C-MPn. Bonding to phosphorus splits the 13C peak in the NMR spectrum. Thus, the C-1 peak is split and the C-2 peak is not. Glycerol, a component of the assay mixture, is also observed in the 13C spectrum. The 13C label is indicated by a red asterisk.