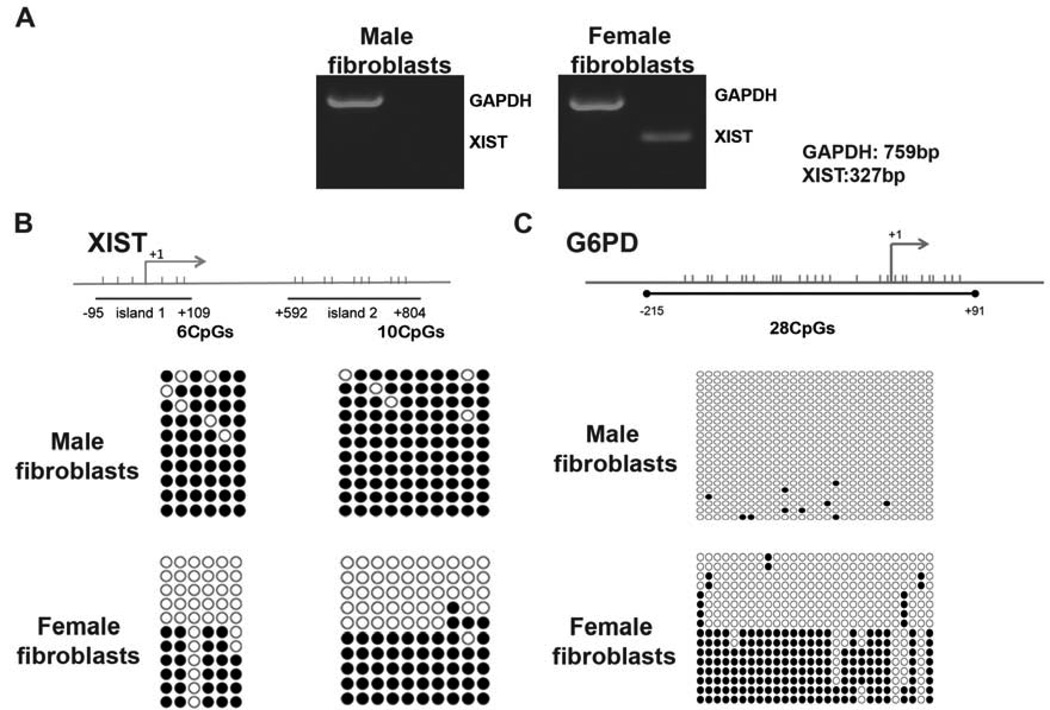
Figure 1. Expression and methylation of X-linked genes in rhesus macaque somatic cells.
(A) Expression of XIST was detected by RT-PCR in female but not male fibroblasts. Housekeeping gene GAPDH was used as a control.
(B) Methylation analysis of XIST promoter region by bisulfite sequencing. Horizontal bars indicate position of individual CpG dinucleotides within each region. The islands 1 and 2 consisting of six and ten CpG sites, respectively, were fully methylated in male fibroblasts indicating transcriptional silencing of XIST. However, approximately half of the clones in female fibroblasts were unmethylated suggesting expression of XIST from one X chromosome.
(C) Methylation profile of X-linked G6PD in fibroblasts. A total of twenty-eight CpG sites were analysed that were unmethylated in male samples in agreement with conclusion that males possess single but active X. As expected, half of the clones in female samples were methylated suggesting that one X chromosome is silenced.