Figure 3.
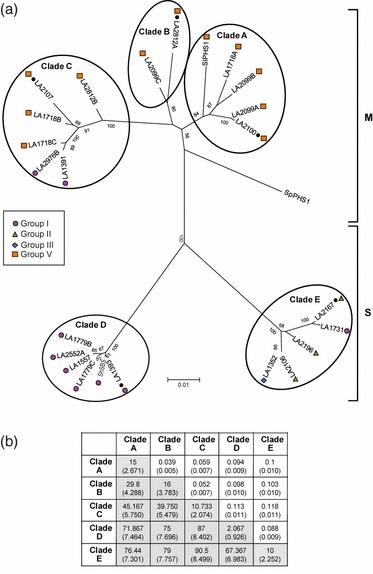
Phylogenetic relationship of TPS20-related sequences from S. habrochaites. (a) An unrooted tree constructed with the ME method using 25 predicted protein sequences, representing a total of 37 sequences from various S. habrochaites accessions (identical sequences at the nucleotide level were eliminated to avoid overcrowding the tree) together with SlPHS1 (FJ797957), SpPHS1 (JN412071), and ShSBS (ACJ38409). Two major groups designated M and S, subdivide into clade A, B and C; and clade D and E, respectively. Bootstrap values above 50 are shown. Colored symbols indicate the chemical group (defined in Figure 2) from which each sequence was isolated. Sequences chosen for codon optimization and expression in E. coli are highlighted (•). (b) Estimates of average evolutionary divergence. Shaded, the number of amino acid differences per sequence from averaging over all sequence pairs within and between each group is shown. White, the p-distance (1-amino acid identity) from averaging over all sequence pairs between groups is shown. Standard error estimates are shown in parentheses. The analysis involved 24 amino acid sequences, corresponding to the five clades shown in (a). Positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. Analyses were conducted in MEGA5.
