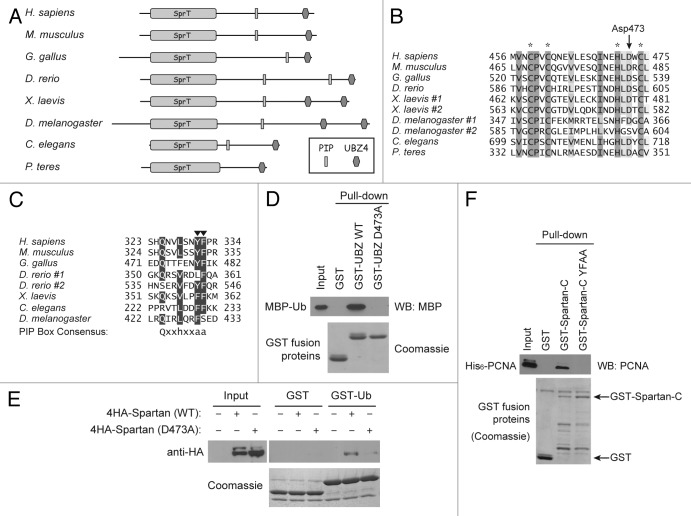
Figure 1. Spartan interacts with ubiquitin and PCNA. (A) Domain structure of Spartan and conservation across species. Putative homologs containing both SprT and UBZ4 domains are shown. (B) Multiple alignment of the UBZ4 domains from Spartan homologs in selected species. Zinc-coordinating residues are highlighted with asterisks. The conserved aspartate residue mutated in this study is indicated by an arrow. (C) Multiple alignment of the PIP boxes from Spartan homologs in selected species. Conserved aromatic residues that were mutated to alanines in this study are indicated by arrowheads. (D) Interaction of the Spartan UBZ4 domain with ubiquitin. In vitro GST pull-down assays were performed using indicated recombinant proteins produced in E. coli. MBP-Ub was examined by western blotting against MBP, and GST-fusion proteins in the precipitates were visualized by Coomassie staining. (E) Interaction of full-length Spartan with ubiquitin. In vitro GST pull-down assays were performed as in (D), except that GST fusion proteins were mixed with 293T cell lysates expressing indicated Spartan proteins. Spartan proteins were examined by western blotting against HA tag, and GST-fusion proteins in the precipitates were visualized by Coomassie staining. (F) Interaction of the Spartan C-terminal fragment with PCNA. In vitro GST pull-down assays were performed using the indicated recombinant proteins produced in E. coli. PCNA was examined by western blotting, and GST-fusion proteins in the precipitates were visualized by Coomassie staining.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.