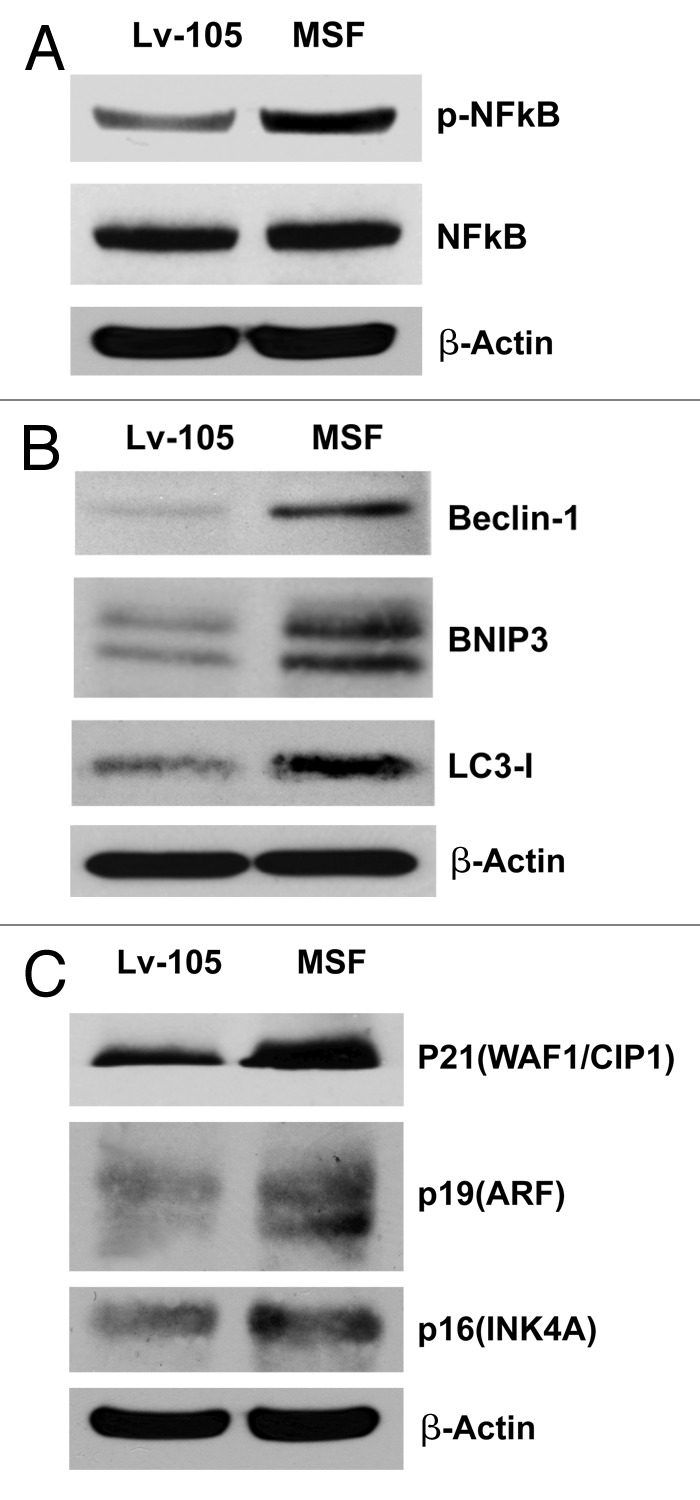
Figure 3. MSF overexpression in fibroblasts promotes the activation of NFκB, increases autophagy, and induces CDK inhibitors. (A) Since the human Rac-1 and Cdc42 proteins efficiently induce the transcriptional activity of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), we next evaluated if MSF is able to induce not only the upregulation of the two small GTPases, but also the activation of NFκB. Note that immunoblot analysis of control or MSF fibroblasts revealed that the levels of p-NFκB are significantly increased in MSF fibroblasts, as compared with control fibroblasts. (B) NFκB can induce autophagy, so we verified if activation of NFκB by MSF overexpressed fibroblasts is sufficient to induce autophagy. Cells were lysed and subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies directed against a panel of autophagy markers. β-actin was used as equal loading control. Note that MSF increases the expression of several key autophagy markers, namely Beclin-1, BNIP3, and LC3-I. (C) To determine if MSF expression is also associated with senescence, we investigated whether known CDK inhibitors are upregulated. Immunoblot analysis shows that p21 (WAF1/CIP1), p19(ARF) and p16(INK4A) are all upregulated, consistent with cell cycle arrest and/or the onset of senescence.
