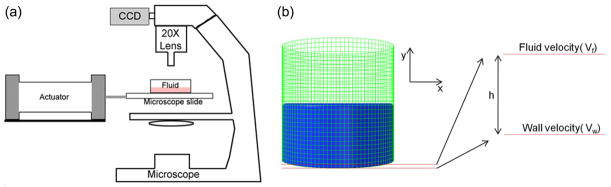
Figure 1. Experimental and computational methods used to describe fluid motions at the well bottom.
(a) Schematic of the Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) setup. A high-speed camera recorded the motions of 1μm red fluorescent polystyrene particles vibrating within a fluid filled chamber attached to a microscope slide. Fluid shear was quantified by comparing the motion of the slide surface to the particle motions measured at 37.5μm distance intervals. (b) A fluid filled cell culture well was modeled as viscous fluid within a rigid well with the Finite Element Method (FEM). Vibration induced fluid shear at the bottom of the well was calculated by computing the relative velocity between wall and fluid assuming linear velocity gradients.