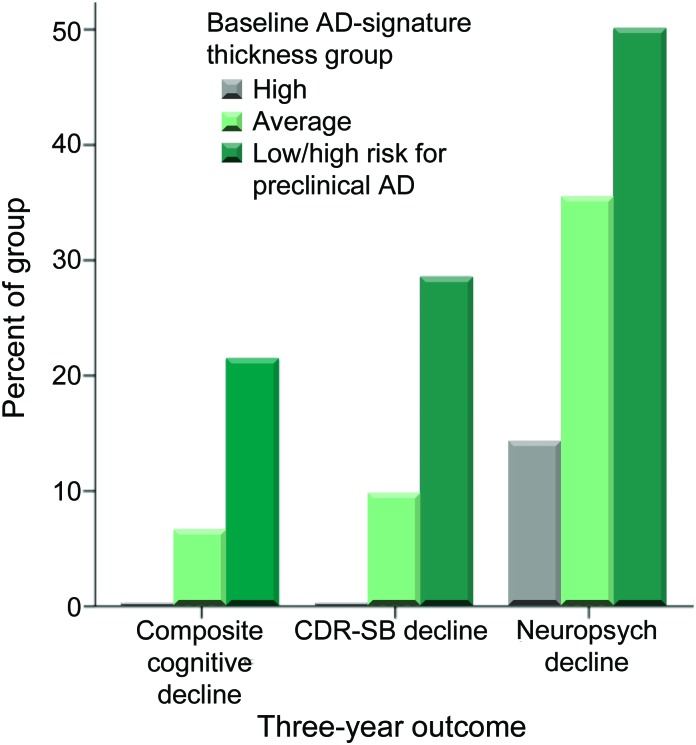
Figure 2. Expression of cortical signature of Alzheimer disease (AD) is associated with future cognitive decline.
Participants who were cognitively normal at baseline but classified as high risk for preclinical AD on the basis of having low AD-signature cortical thickness were at markedly elevated risk of meeting the 3-year cognitive decline outcome (composite cognitive decline) as compared with participants with average or high AD-signature cortical thickness. Similar findings were present when the individual CDR–sum of boxes (CDR-SB) decline outcome or the neuropsychological performance decline outcome were examined.