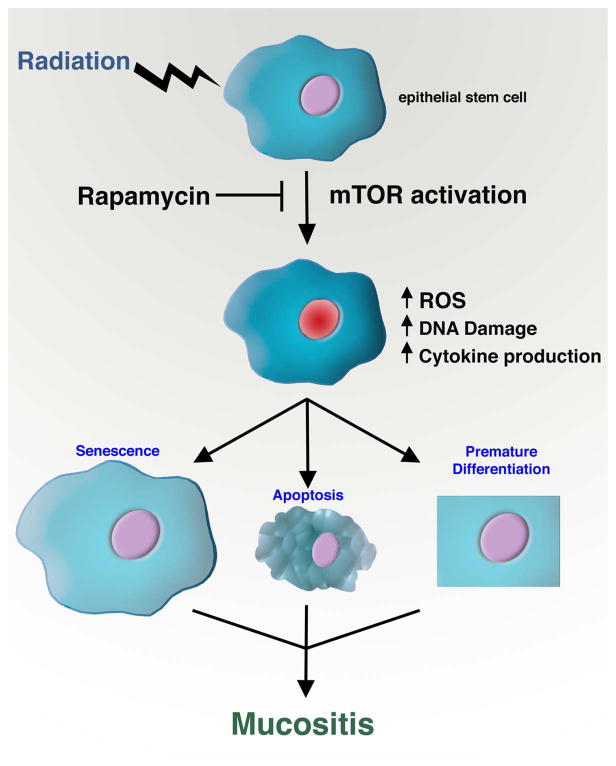
Figure 1.
The role of mTOR in radiation-induced mucositis. Irradiation of epithelial stem cells leads to mTOR activation. Inhibiting this activation with rapamycin treatment reduces the levels of ROS, inflammatory cytokine production and overall DNA damage and thereby prevents radiation-induced senescence. Rapamycin may also protect against the premature differentiation or apoptosis of stem and progenitor cells. These protective effects combine to prevent the appearance of clinically debilitating side-effects such as mucositis.