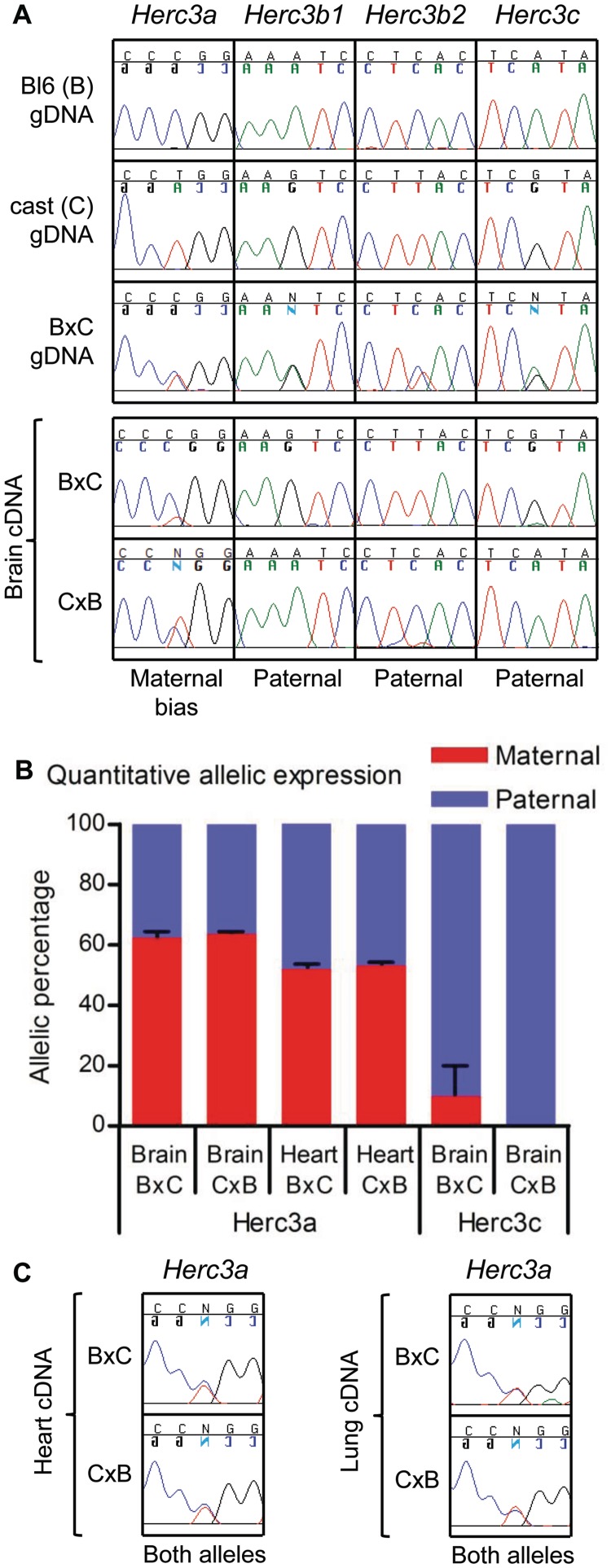
Figure 2.
Allele-specific use of poly(A) sites. (A) Primer pairs unique to each of the Herc3 transcript variants were used in RT-PCR on RNA isolated from whole brains of inter-subspecies mouse hybrids (Bl6 [B] and cast [C]). Amplicons were sequenced across SNPs to determine parent-of-origin specific expression. The SNP is the centre nucleotide of each trace. In each cross, the maternal strain is presented first. Performing the experiment on the reciprocal cross confirms true imprinted expression, rather than a preference for expression from either the Bl6 or cast alleles. The relevant genomic DNA (gDNA) sequences of the parental strains and of a B × C hybrid are shown at the top of the figure. The allele on which the poly(A) site associated with each transcript is utilized is indicated below each panel of traces (maternal bias or paternal). Some of the base calls are presented as a mirror image; this reflects the sequencing of some amplicons in the reverse orientation and does not influence the interpretation of the data. (B) Quantification of allele-specific expression of Herc3a and Herc3c using pyrosequencing over Bl6/cast SNPs (see Materials and Methods for details). In neonatal brain, Herc3a is expressed with a bias from the maternal allele (62:38 maternal:paternal ratio) but is expressed approximately equally from the two alleles in heart (52:48 maternal:paternal ratio). This is the case for samples from both B × C and C × B intercrosses. As a control, Herc3c, shown in (A) to be paternally expressed in brain, shows expression exclusively from the paternally derived allele in C × B brain and >90% paternal expression in B × C brain, confirming the sensitivity of this approach in determining allele-specific expression. Error bars indicate the standard error of the percent maternal expression values from biological replicates. (C) Sequence traces showing that transcripts utilizing the downstream poly(A) site (Herc3a transcripts) are derived equally from the two parental alleles in heart and lung.