Figure 1.
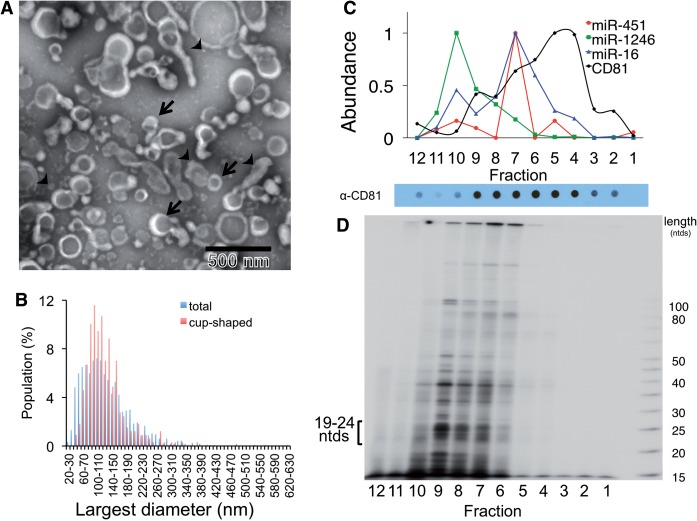
MiRNAs exported from breast cancer cells associate with a complex population of particles. (A) Particulate complexes collected from MDA-MB-231 cells grown in defined media were cleared of debris, filtered, collected by centrifugation at 70 000g (P70) and imaged by negative-stain EM. The preparation contains cup-shaped vesicles (as indicated by arrows) and structures of different shapes (arrowheads). (B) The largest diameter (ø) of >500 structures was measured and plotted. (C) A P70 preparation of MDA-MB-231 cells was subjected to buoyant sucrose gradient centrifugation for 18 h, and 1 ml gradient fractions (12, bottom of gradient, 1, top) were assayed for miRNA and CD81 abundance. The miRNA species of each gradient fraction were quantified using TaqMan qRT–PCR, and each miRNA species is plotted as a proportion of the fraction with maximum miRNA abundance, set at 1, and CD81 was measured using a dot blot probed with anti-CD81 antibody, and binding of a secondary goat-anti-mouse IgG-Alexa 488 was measured by fluorescence quantitation as described in Materials and Methods. A dot blot developed for secondary HRP antibody binding is shown below the graph. (D) Total small RNAs were visualized after 32P end-labeling and separation by native PAGE. 19–24 ntds: RNA species with expected size for miRNAs.