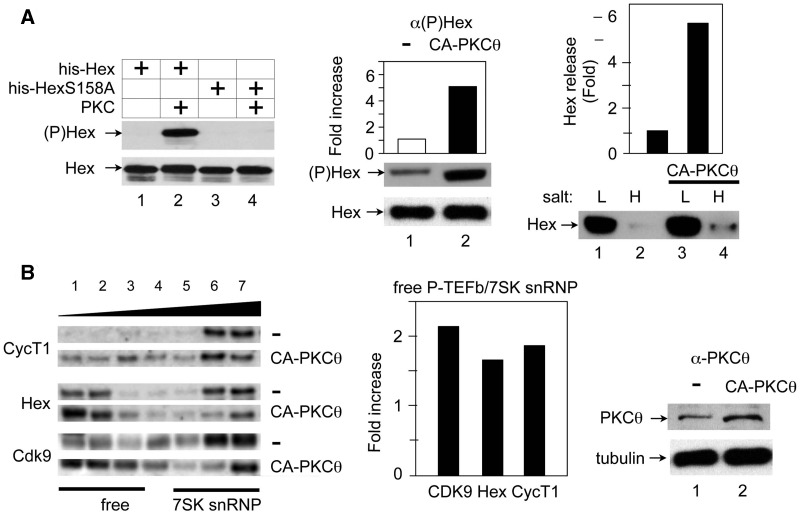
Figure 5.
The CA-PKCθ protein phosphorylates HEXIM1, which releases free P-TEFb. (A) The CA PKCθ protein (CA-PKCθ) phosphorylates HEXIM1 and leads to its release in cells. Left panel: Evaluation of antibodies against HEXIM1, which is phosphorylated on the serine at position 158 ((P)Hex). IVKAs were performed with purified PKC and WT HEXIM1 or mutant HEXIM1 (S158A) proteins (Hex or HexS158A) and non-radioactive ATP as the substrate. Protein complexes were then separated by SDS–PAGE, followed by western blotting with anti-phospho-HEXIM1 ((P)Hex, upper panel) and anti-HEXIM1 (Hex, lower panel) antibodies. Center and right panels: Cell fractionation analyses were performed with Jurkat T cells, which expressed the empty plasmid vector (−) or the CA PKCθ protein (CA-PKCθ). Complexes, which were bound loosely or tightly to chromatin were extracted with buffers containing low (L,10 mM) and high (H, 300 mM) salt concentrations. Center panel: Phosphorylated and unphosphorylated HEXIM1 proteins (middle panel, (P)Hex; bottom panel, Hex) in the high salt (H) fraction was detected with anti-phospho-HEXIM1 and anti-HEXIM1 antibodies, respectively. Band intensities were quantified (top panel) and are presented as fold increase over the value obtained with Jurkat T cells, which expressed only the empty plasmid vector. Right panel: After fractionation, HEXIM1 was detected with anti-HEXIM1 antibodies by western blotting (lower panel, Hex). The release of HEXIM1 to chromatin (H, high salt) was quantified relative to the value obtained with Jurkat T cells, which expressed the empty plasmid vector only (Hex release). (B) The CA PKCθ protein (CA-PKCθ) releases of P-TEFb and HEXIM1 from 7SK snRNP. Left panel: Glycerol gradient sedimentation was performed with Jurkat T cells, which expressed the empty plasmid vector (upper panels, −) or CA-PKCθ (lower panels, CA-PKCθ). Twenty-four hours after transfection, cell lysates were subjected to glycerol gradient (10–30%) sedimentation. Fractions were separated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed with anti-CycT1 (top panels), anti-HEXIM1 (middle panels) and anti-CDK9 (bottom panels) antibodies by western blotting. Center Panel: Band intensities in fractions corresponding to free P-TEFb (lanes 1–3) and 7SK snRNP (lanes 5–7) were quantified and ratios between these two groups were calculated and plotted as a fold-increase over values obtained with untransfected Jurkat cells. Right panel: The expression of CA-PKCθ was confirmed with anti-PKCθ antibodies by western blotting.