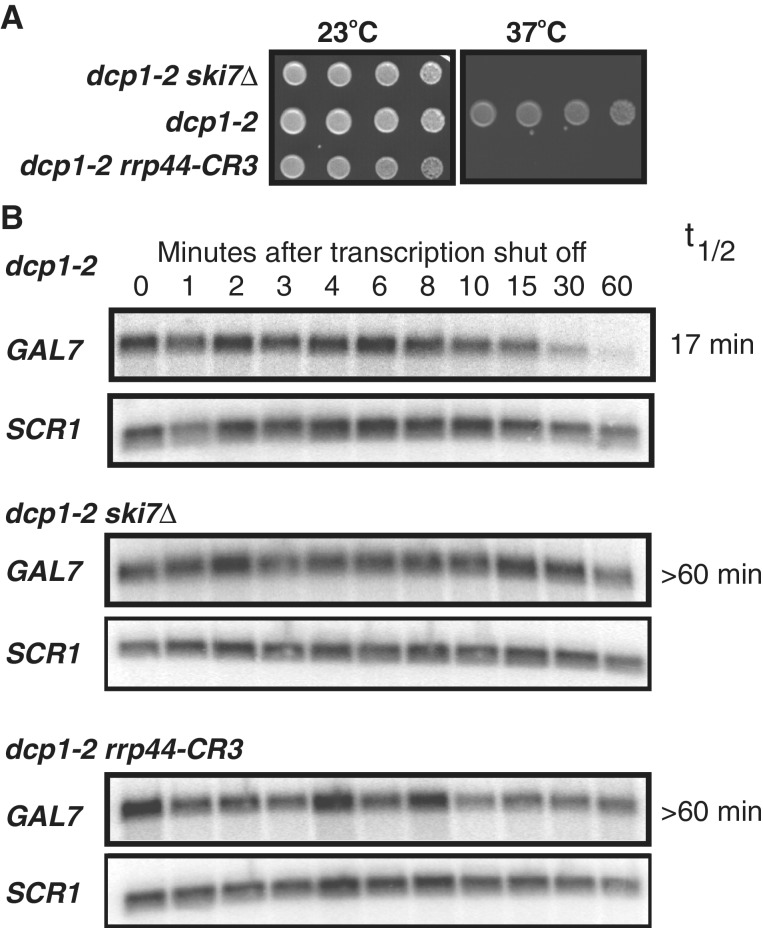
Figure 4.
Simultaneously mutating the three conserved Cys residues of Rrp44p to Ser stabilizes cellular mRNAs. (A) The rrp44–CR3 mutation is synthetically lethal with a temperature-sensitive mutation in the decapping enzyme, dcp1–2. The experiment was performed as described for Figures 2 and 3. (B) The rrp44–CR3 mutation reduces the rate of exosome-mediated degradation of the GAL7 mRNA. duplicate cultures of the indicated strains were grown in media containing galactose, and then incubated for 1 h at 37°C to inactivate the decapping enzyme. The media was then replaced with media containing glucose to shut off transcription of the GAL7 gene and RNA was isolated at the indicated time points and analyzed by northern blotting. The RNA subunit of the signal recognition particle (encoded by the SCR1 gene) was used as a loading control. RNA levels were quantitated using a STORM PhosphoImager and half-lives determined. Both half-life measurements for the dcp1–2 strain were 17 min. In the dcp1–2 ski7Δ and dcp1–2 rrp44–CR3 strains the half-lives were more than 60 min.