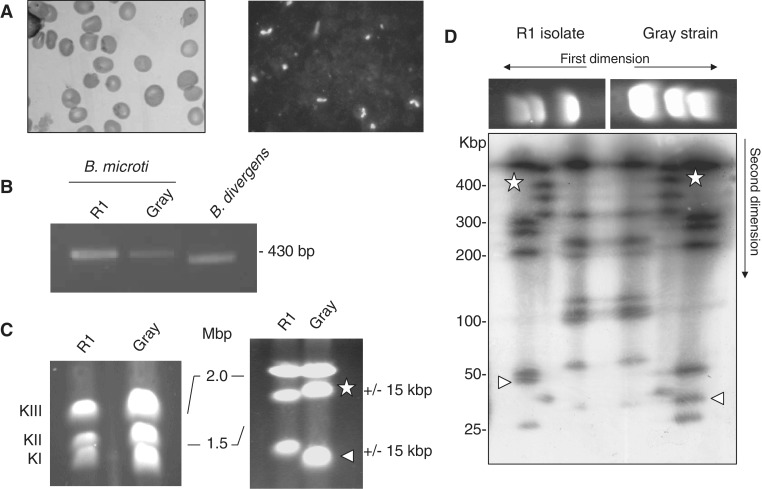
Figure 1.
Babesia microti strain R1 characterization. (A) Light-microscopy analysis of B. microti infected blood. Left: blood smear. Right: immunofluorescence analysis using serum from a hamster infected with the B. microti Gray standard laboratory strain. Similar serum was used for serological assays. (B) PCR amplification of the ssu gene using PIRO-A and PIRO-B primers (77). These primers amplify a 436 bp fragment in B. microti Gray and R1 strains and a 408 bp fragment in B. divergens Rouen strain. The integrity of the PCR fragment was confirmed by DNA sequencing. (C) B. microti karyotype. PFGE conditions used are: left, 0.7% agarose, 400 s pulses for 55 h; right, 1% agarose, 200 s pulses for 65 h. Length polymorphism between the R1 isolate and the Gray strain is observed on chromosome 1 and 2. (D) 2D-PFGE NotI Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) analysis of B. microti. Each chromosome length polymorphism results from a single RFLP of 15 kbp (see triangle and star for chromosome I and II respectively). The genome structure of Gray and R1 strain may differ from each other only with a single recombination event. PFGE conditions used are: 1.2 % agarose gel, pulse conditions, 5 s for 8 h, 15 s for 7 h and 30 s for 6 h, tension, 6.5 V/cm.