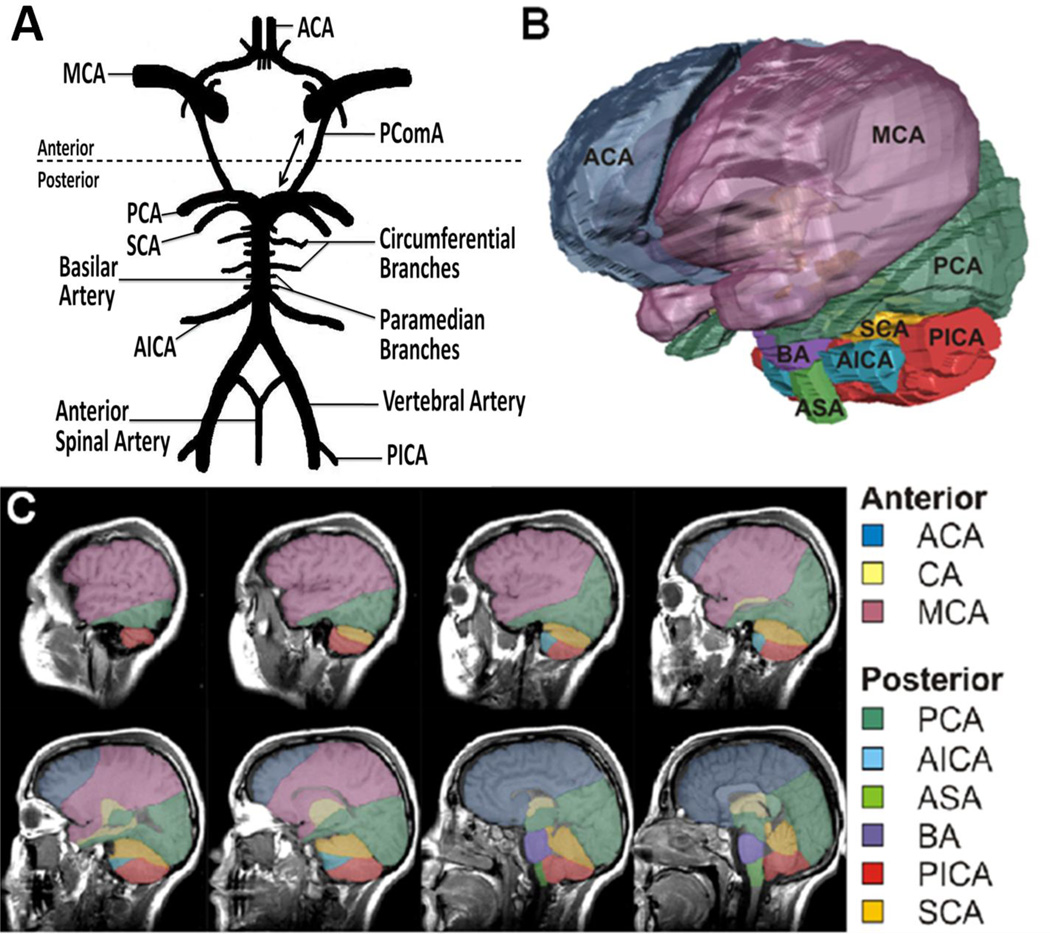
Figure 1.
Illustrations are showing vascular distributions within the human brain. (A) The circle of Willis supplies abundant collateral circulation to the forebrain and hindbrain. Dotted line demarcates anterior /posterior circulation separation at posterior communicating artery (PComA). Double-headed arrow indicates potential reversal of flow across PComA. (B) Volumetric 3-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of the human brain: color-coded to display predominant vascular distributions. (C) Serial sagittal sections demonstrating depth dependant distribution of the respective circulations. ACA indicates anterior cerebral artery; CA, carotid artery; MCA, middle cerebral artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; AICA, anterior inferior cerebellar artery; ASA, anterior spinal artery; BA, basilar artery; PICA, posterior inferior cerebellar artery; SCA, superior cerebellar artery