Figure 2.
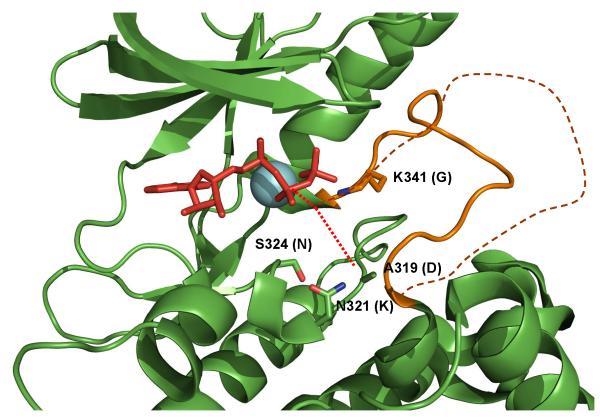
Pseudoactive site features of ILK: A non-degraded ATP is bound to ILK KLD but its g-phosphate is oriented far away from A319 (see the dotted red line) – a site corresponding to the conventional catalytic base Asp. The typical DFG is replaced by DVK where K341 forms the salt-bridge with the g-phosphate of ATP, facilitating its distinct orientation. In addition to A319 that replaces the conventional catalytic Asp, multiple other catalytically important residues are missing including N321 that replaces Lys and S324 that replaces Asn. These catalytic residues are labeled and their corresponding catalytic residues are provided in the parentheses. Note that there are no surrounding residues that may alternatively substitute these catalytic residues. A single magnesium (cyan) is present in ILK KLD but coordinated differently in contrast to the two magnesium ions present in the conventional kinases. Finally, the activation segment (solid orange line) of ILK KLD is much shorter than the conventional one (dotted orange line).