Abstract
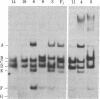
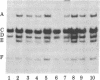
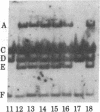
The ribosomal genes (rDNA) in mouse inbred strains have a multichromosomal distribution. Using a structural feature of rDNA [variable length rDNA segment (VrDNA)] that shows length polymorphism within and among inbred strains, we studied the chromosomal distribution of the variant ribosomal gene type through genetic analysis. Our results show that five of the length variant classes can be divided into three discrete linkage groups. The variants present on a particular chromosome pair appear to be unique to that pair and absent from nonhomologous chromosomes. The chromosomal location of particular variants appears to be the same in two unrelated inbred strains suggesting that the observed linkage patterns predate the origin of inbred mice. The nonrandom chromosomal distribution of these rDNA classes suggests that only a limited degree of genetic exchange occurs among nucleolus organizer regions on nonhomologous chromosomes. We have localized one particular VrDNA linkage group to chromosome 12. These and other restriction fragment polymorphisms can be used in the construction of detailed mouse linkage maps.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheim N. Characterization of mouse ribosomal gene fragments purified by molecular cloning. Gene. 1979 Oct;7(2):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Kuehn M. The genetic behaviour of a cloned mouse ribosomal DNA segment mimics mouse ribosomal gene evolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 15;134(4):743–763. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey D. W. Recombinant-inbred strains. An aid to finding identity, linkage, and function of histocompatibility and other genes. Transplantation. 1971 Mar;11(3):325–327. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197103000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dev V. G., Tantravahi R., Miller D. A., Miller O. J. Nucleolus organizers in Mus musculus subspecies and in the RAG mouse cell line. Genetics. 1977 Jun;86(2 Pt 1):389–398. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsevier S. M., Ruddle F. H. Location of genes coding for 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA within the genome of Mus musculus. Chromosoma. 1975 Oct 14;52(3):219–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00332112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodpasture C., Bloom S. E. Visualization of nucleolar organizer regions im mammalian chromosomes using silver staining. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 20;53(1):37–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00329389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gropp A., Tettenborn U., von Lehmann E. Chromosomenvariation vom Robertson'schen Typus bei der Tabakmaus, M. poschiavinus, und ihren Hybriden mit der Laboratoriumsmaus. Cytogenetics. 1970;9(1):9–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Eicher E. M., Yu M. T., Atwood K. C. Variation in ribosomal RNA gene number in mouse chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1976;17(6):307–316. doi: 10.1159/000130733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H., Arnheim N. Human nucleolus organizers on nonhomologous chromosomes can share the same ribosomal gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Banerji J., Penncavage N. A., Lang R., Arnheim N. 5' flanking region of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes displays length heterogeneity in germlines of inbred mouse strains. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Tantravahi R., Dev V. G., Miller O. J. Q- and C-band chromosome markers in inbred strains of Mus musculus. Genetics. 1976 Sep;84(1):67–75. doi: 10.1093/genetics/84.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staats J. Standardized nomenclature for inbred strains of mice: sixth listing. Cancer Res. 1976 Dec;36(12):4333–4377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartof K. D., Dawid I. G. Similarities and differences in the structure of X and Y chromosome rRNA genes of Drosophila. Nature. 1976 Sep 2;263(5572):27–30. doi: 10.1038/263027a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., Bedigian H. G., Meier H. Genetic studies of the Fv-1 locus of mice: linkage with Gpd-1 in recombinant inbred lines. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):106–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.106-109.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellauer P. K., Dawid I. B., Tartof K. D. X and Y chromosomal ribosomal DNA of Drosophila: comparison of spacers and insertions. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagura T., Yagura M., Muramatsu M. Drosophila melanogaster has different ribosomal RNA sequences on S and Y chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 9;133(4):533–547. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90406-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]