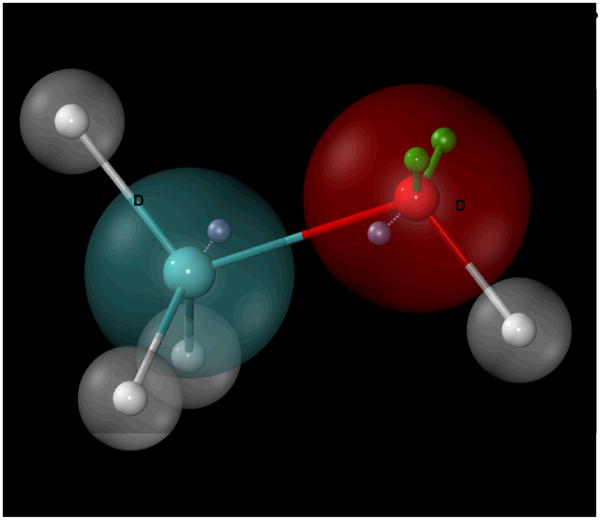
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of how atomic polarizability is treated in the CHARMM polarizable force field using methanol as an example. Drude oscillators (or particles)(blue, “D”) are attached to non-hydrogen parent atoms through harmonic bonds (dashed lines). Oxygen lone-pairs (green, “LP”) are connected with constrained bonds, angles, and dihedrals relative to the C-O-H plane. Hydrogens are not considered as polarizable entities in this model.