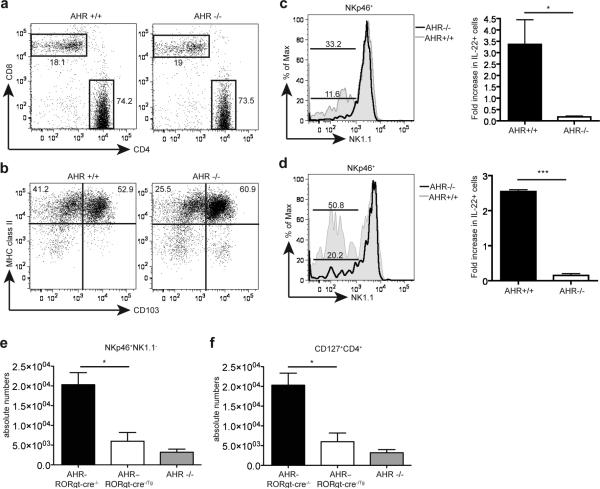
Figure 4.
The developmental defect of AHR-/- mice is cell-intrinsic. (a,b) siLP from AHR-/- and AHR+/+ mice were harvested and analyzed by FACS for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (a) and dendritic cell populations (b). Cells are gated on CD3+ lymphocytes (a) and on CD19-CD11c+ populations (b). (c) siLP cells from AHR-/- into wildtype and wildtype into wildtype bone marrow (BM) chimeras were harvested and analyzed by FACS. Cells are gated on CD45.2+CD3-CD19-CD4-NKp46+. The bottom bar represents percent of NKp46+NK1.1- cells from AHR-/- reconstituted cells, and top bar represent percent of NKp46+NK1.1- cells from AHR+/+ reconstituted cells. Right panel represents fold increase in IL-22+ cells from IL-23 stimulated cells gated on CD3-CD19-NKp46+ cells from AHR-/- and AHR+/+ chimeras (n=4). AHR-/- BM reconstituted mice show reduced frequencies of NKp46+ILC compared to WT BM reconstituted mice. The reconstitution of WT NKp46+ILC in irradiated WT mice was incomplete. (d) siLP cells from mixed AHR-/- and WT bone marrow chimeras were analyzed by gating on CD45.2+CD3-CD19-CD4-NKp46+ (AHR-/-) cells and CD45.2-CD3-CD19-CD4-NKp46+ (AHR+/+) cells and reconstitution of NKp46+ILC were compared. Bottom bar represent percent of NKp46+NK1.1- cells in AHR-/- cells, and top bar represent percent of NKp46+NK1.1- cells in AHR+/+ cells. Right panel represents fold increase in IL-22+ from IL-23 stimulated cells gated on CD3-CD19-NKp46+ from AHR-/- and AHR+/+ mixed chimeras. (n=3) (e,f) Cells isolated from the siLP of control (AHR-RORγt-cre-/-) and AHR conditional deletion (AHR–RORγt-cre-/Tg) mice were harvested and analyzed by FACS for NKp46+ ILC (e) and CD4+ LTi-like ILC (f) populations. Graphs show absolute numbers of cells. (n=4) Cells were also compared to absolute numbers of NKp46+ ILC (e) and CD4+ LTi-like ILC (f) populations from AHR-/- siLP from (supplementary fig. 4)