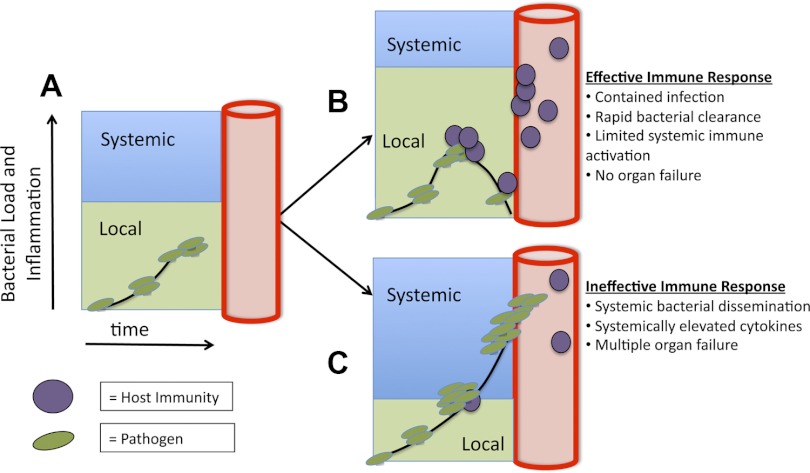
Fig. 3.
Sepsis is a numeric and geographic race between bacterial growth and host defense. A: after the initial inoculum, bacteria or other pathogens begin to propagate within local compartments. B: if the immune response is sufficiently fast, then the spread of pathogens is limited by defense mechanisms, including NET formation, local thromboses, and neutrophil and monocyte recruitment. C: in contrast, if invading pathogens are able to spread outside a single compartment and the inflection point where specific host defense mechanisms shift from benefit to detriment is crossed, then both infection and the inflammatory response to the infection become systemic, resulting in diffuse organ injury and shock.