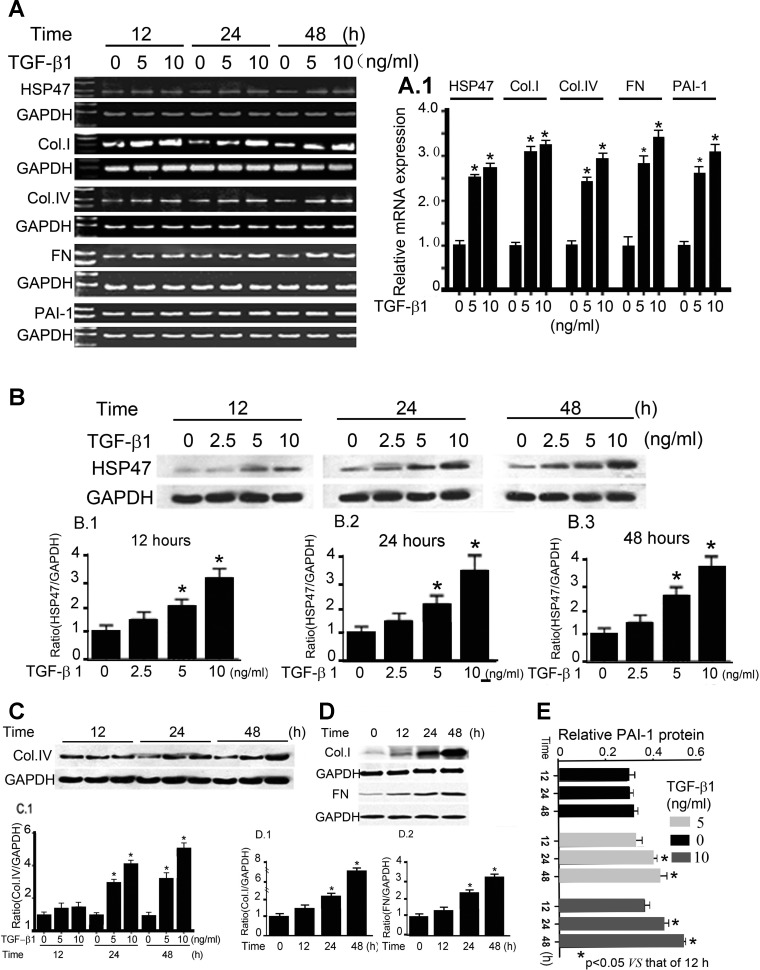
Fig. 2.
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1-induced increased expression of HSP47, Col.1, Col.IV, FN, and PAI-1 in HK-2 cells. HK-2 cells were maintained for 12–48 h and treated with various concentrations of TGF-β1 (0–10 ng/ml), and the expression of HSP47, Col.I, Col.IV, FN, and PAI-1 was evaluated. A: RT-PCR analyses revealed increased mRNA expression of HSP47, Col.I, Col.IV, FN, and PAI-1 with treatment with TGF-β1. No discernible changes in GAPDH expression were observed. A,1: mRNA expression of HSP47, Col.I, Col.IV, FN, and PAI-1 relative to GAPDH, as shown in A. Values are expressed as means ± SE; n = 4. *P < 0.01 vs. the control group. B: Western blots (top) and the respective densitometric analyses of the bands (1–3) showing the dose- and time-dependent increases in the expression of HSP47 in HK-2 cells after TGF-β1 treatment. Values are expressed as means ± SE; n = 5. *P < 0.01 compared with the control group. C and D: TGF-β1 treatment also increased the protein expression of Col.IV, Col.I, and FN in HK-2 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The bar graphs in C,1, D,1, and D,2 represent densitometric analyses of the top Western blots. Values were normalized against the GAPDH control and are expressed as means ± SE; n = 5. *P < 0.01. E: ELISA methods revealed that TGF-β1 increases PAI-1 expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner in HK-2 cells. Values are expressed as means ± SE; n = 6. *P < 0.01 vs. 12-h TGF-β1 treatment.