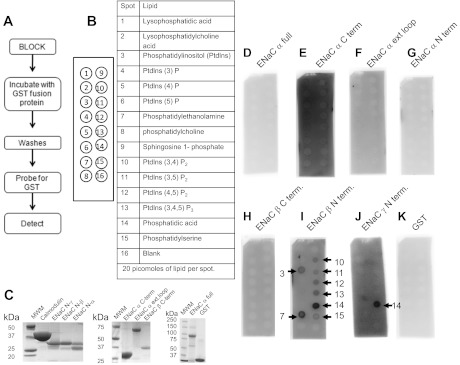
Fig. 2.
Phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP) strip overlay binding assay using recombinant Xenopus GST-ENaC fusion proteins. Schematic of the general procedure (A) and format (B) of the PIP strip binding assay. C: Coomassie-stained gel showing the purity and size of each recombinant protein used. GST fusion proteins of full length Xenopus ENaC-α (D), Xenopus ENaC-α carboxy-terminal domain (E), Xenopus ENaC-α extracellular loop domain (F), Xenopus ENaC-α amino-terminal domain (G), and Xenopus ENaC-β carboxy-terminal domain (H) did not directly bind to any of the 15 different phospholipids or banks. GST fusion proteins of Xenopus ENaC-β amino-terminal domain (I) and Xenopus ENaC-γ amino-terminal domain (J) directly bound to various phospholipids, but with different affinities. GST alone did not bind with any appreciable affinity to any of the spotted phospholipids (K). The white dots present in various spots are due to burnout of the signal of the film.