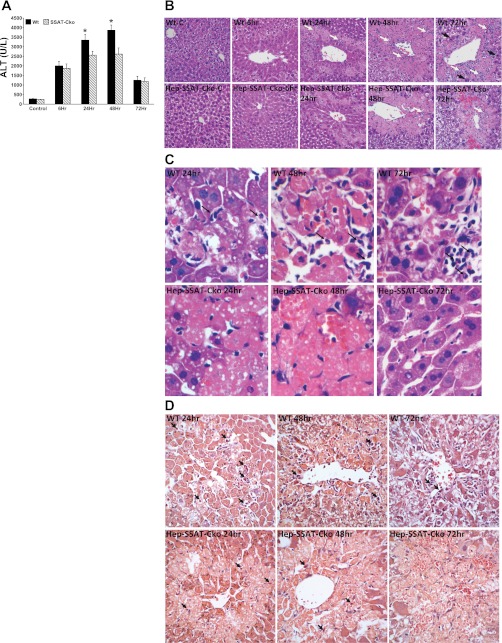
Fig. 4.
Assessing the effect of hepatocyte-specific SSAT deficiency on the severity of CCl4-induced liver injury. WT and Hep-SSAT-Cko were given intraperitoneal injections of CCl4 or vehicle. Animals (n = 6/treatment group/genotype) were killed at timed intervals after treatment. A: serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels of control and CCl4-treated WT and Hep-SSAT-Cko mice (n = 6/group) were compared following the protocol outlined in materials and methods. *P < 0.05 WT compared with SSAT-Cko. B: liver histology (magnification, ×400) of control and injured animals from both genotypes were compared. Infiltrating neutrophils (small white arrows), chronic inflammatory cells (large white arrows) and mitotic bodies (large black arrows) are marked. C: liver histology of CCl4-treated WT and Hep-SSAT-Cko mice was examined at ×600 magnification (black arrows mark the infiltrating neutrophils). D: livers of CCl4-treated WT and Hep-SSAT-Cko mice were subjected to chloroacetate estrase staining to identify the infiltrating neutrophils (black arrows).